In Vivo Red Blood Cells/Plasma Partition Coefficient of Treosulfan and Its Active Monoepoxide in Rats
- PMID: 29542019
- PMCID: PMC6133075
- DOI: 10.1007/s13318-018-0469-7
In Vivo Red Blood Cells/Plasma Partition Coefficient of Treosulfan and Its Active Monoepoxide in Rats
Abstract
Background and objectives: Treosulfan is a prodrug applied in the treatment of ovarian cancer and conditioning prior to stem cell transplantation. So far, the bioanalysis of treosulfan in either whole blood or red blood cells (RBC) has not been carried out. In this work, the RBC/plasma partition coefficient (Ke/p) of treosulfan and its active monoepoxide was determined for the first time.
Methods: Male and female 10-week-old Wistar rats (n = 6/6) received an intraperitoneal injection of treosulfan at the dose of 500 mg/kg body weight. The concentrations of treosulfan and its monoepoxide in plasma (Cp) and RBC were analyzed with a validated HPLC-MS/MS method.
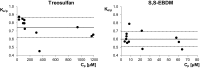
Results: The mean Ke/p of treosulfan and its monoepoxide were 0.74 and 0.60, respectively, corresponding to the blood/plasma partition coefficient of 0.88 and 0.82. The Spearman test demonstrated that the Ke/p of the prodrug correlated with its Cp, but no correlation between the Ke/p and Cp of the active monoepoxide was observed.
Conclusions: Treosulfan and its monoepoxide achieve higher concentrations in plasma than in RBC; therefore, the choice of plasma for bioanalysis is rational as compared to whole blood. The distribution of treosulfan into RBC may be a saturable process at therapeutic concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors, M. Romański, A. Zacharzewska, A. Teżyk, and F.K. Główka, have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The studies were approved by the Local Ethics Committee for Experimental on Animals in Poznan, Poland (Approval no. 11/2016).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disposition of treosulfan and its active monoepoxide in a bone marrow, liver, lungs, brain, and muscle: Studies in a rat model with clinical relevance.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Nov 15;109:616-623. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28916482
-
Formation Rate-Limited Pharmacokinetics of Biologically Active Epoxy Transformers of Prodrug Treosulfan.J Pharm Sci. 2016 May;105(5):1790-1797. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27044946
-
Pharmacokinetics of treosulfan and its active monoepoxide in pediatric patients after intravenous infusion of high-dose treosulfan prior to HSCT.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Feb 20;68:87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.12.010. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25527118 Clinical Trial.
-
Treosulfan Pharmacokinetics and its Variability in Pediatric and Adult Patients Undergoing Conditioning Prior to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Current State of the Art, In-Depth Analysis, and Perspectives.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Oct;57(10):1255-1265. doi: 10.1007/s40262-018-0647-4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29557088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical bioanalysis of treosulfan and its epoxides: The importance of collected blood processing for valid pharmacokinetic results.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 May 10;153:199-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.02.049. Epub 2018 Feb 24. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29501039 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of Interpatient Variability in Treosulfan Pharmacokinetics in AML Patients Undergoing Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8215. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158215. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125785 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the drug-drug interaction potential of treosulfan using a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modelling approach.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;88(4):1722-1734. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15081. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34519068 Free PMC article.
-
The discovery of berberine erythrocyte-hemoglobin self-assembly delivery system: a neglected carrier underlying its pharmacokinetics.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):856-870. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2036870. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35277093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sehouli J, Tomè O, Dimitrova D, Camara O, Runnebaum IB, Tessen HW, Rautenberg B, Chekerov R, Muallem MZ, Lux MP, Trarbach T, Gitsch G. A phase III, open label, randomized multicenter controlled trial of oral versus intravenous treosulfan in heavily pretreated recurrent ovarian cancer: a study of the North-Eastern German Society of Gynecological Oncology (NOGGO) J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017;2017(143):541–555. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2307-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Treosulfan Injection (medac UK)—Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC). https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/6431. Accessed 5 Jan 2018.
-
- Treosulfan Capsules 250 mg—Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)—(eMC). https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/6426. Accessed 5 Jan 2018.
-
- Burroughs LM, Shimamura A, Talano JA, Domm JA, Baker KK, Delaney C, Frangoul H, Margolis DA, Baker KS, Nemecek ER, Geddis AE, Sandmaier BM, Deeg HJ, Storb R, Woolfrey AE. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation using treosulfan-based conditioning for treatment of marrow failure disorders. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:1669–1677. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.06.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

