Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System
- PMID: 29543776
- PMCID: PMC5877737
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030876
Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System
Abstract
For many years, modulators of the renin angiotensin system (RAS) have been trusted by clinicians for the control of essential hypertension. It was recently demonstrated that these modulators have other pleiotropic properties independent of their hypotensive effects, such as enhancement of cognition. Within the brain, different components of the RAS have been extensively studied in the context of neuroprotection and cognition. Interestingly, a crosstalk between the RAS and other systems such as cholinergic, dopaminergic and adrenergic systems have been demonstrated. In this review, the preclinical and clinical evidence for the impact of RAS modulators on cognitive impairment of multiple etiologies will be discussed. In addition, the expression and function of different receptor subtypes within the RAS such as: Angiotensin II type I receptor (AT1R), Angiotensin II type II receptor (AT2R), Angiotensin IV receptor (AT4R), Mas receptor (MasR), and Mas-related-G protein-coupled receptor (MrgD), on different cell types within the brain will be presented. We aim to direct the attention of the scientific community to the plethora of evidence on the importance of the RAS on cognition and to the different disease conditions in which these agents can be beneficial.
Keywords: aging; alzhemiers disease (AD); angiotensin; angiotensin AT1 receptor; angiotensin AT2 receptor; inflammation; mas receptor; mas-related-G protein coupled MrgD receptor; microglia; parkinson’s disease (PD); vascular cognitive impairment (VCI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
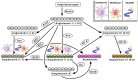
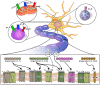
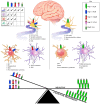
References
-
- Tigerstedt R., Bergman P.G. Niere und Kreislauf. Arch. Physiol. 1898;8:223–227.
-
- Mentz R.J., Bakris G.L., Waeber B., McMurray J.J., Gheorghiade M., Ruilope L.M., Maggioni A.P., Swedberg K., Pina I.L., Fiuzat M., et al. The past, present and future of renin-angiotensin aldosterone system inhibition. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013;167:1677–1687. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.10.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

