Frequent pain in older people with and without diabetes - Finnish community based study
- PMID: 29544464
- PMCID: PMC5856375
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-018-0762-y
Frequent pain in older people with and without diabetes - Finnish community based study
Abstract
Background: The association between pain and diabetes in older people has been largely unexplored. The aim of this survey was to analyze the prevalence and characteristics of pain among Finnish men and women 65 or older with and without diabetes in primary care.
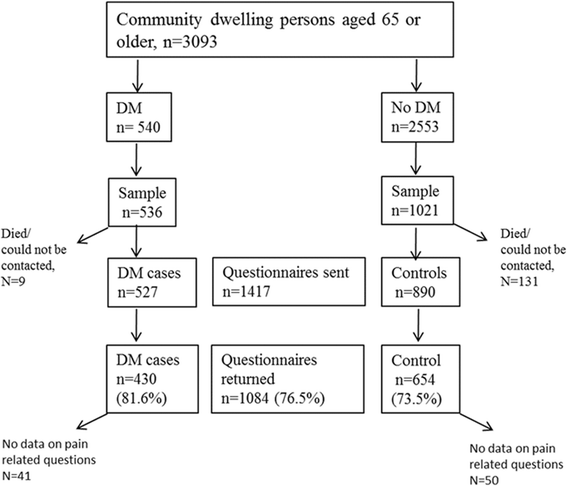
Methods: All home-dwelling persons 65 years or older with diabetes (N = 527) and age and gender matched controls (N = 890) were identified from electronic patient records. Frequent pain was regarded as any pain experienced more often than once a week, and it was divided into pain experienced several times a week but not daily and pain experienced daily or continuously. The Numeric Rating Scale (0-10) (NRS) was used to assess the intensity and interference of the pain.
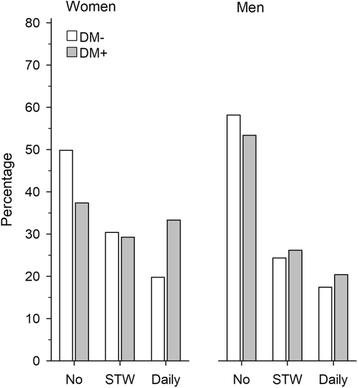
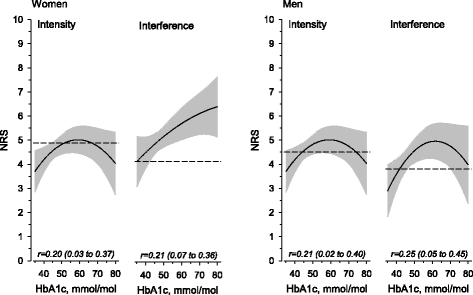
Results: The number of subjects who returned the questionnaire was 1084 (76.5%). The prevalence of frequent pain in the preceding week was 50% among women without diabetes and 63% among women with diabetes (adjusted, p = 0.22). In men, the corresponding proportions were 42% without diabetes and 47% with diabetes (adjusted, p = 0.58). In both genders, depressive symptoms and the number of comorbidities were associated with pain experienced more often than once a week and with daily pain. Diabetes was not associated with pain intensity or pain interference in either women or men.
Conclusions: Pain in older adults is associated with depressive symptoms and the number of comorbidities more than with diabetes itself.
Keywords: Diabetes; Older people; Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol of the ISDM (Inner-Savo Diabetes Mellitus) study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Northern Savo Hospital District, Kuopio, Finland (256/2015). The study was approved by the Inner Savo Health Care Federation of Municipalities (61 A/2015). The questionnaire included information letter about the use of data and returning of questionnaire was voluntary. The autonomy of research subjects was respected and only anonymous data were analyzed. No harm was possible for the subjects and confidentiality of the subjects and research data were protected.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declares that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Global report on diabetes 2016, 2016. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204874/1/WHO_NMH_NVI_16.3_eng.p.... Accessed 10 Apr 2017.
-
- Laakso M, Groop L, Isomaa B, Honkasalo M, Juselius P, Lindström J, et al. Update on current care guideline diabetes. Duodecim. 2016;132:881–882. - PubMed
-
- Mäntyselkä P, Korniloff K, Saaristo T, Koponen H, Erikson J, Puolijoki H, et al. Association of depressive symptoms with impaired glucose regulation, screen-detected and previously known type 2 diabetes: findings from the Finnish D2D survey. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:71–76. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

