Comprehensive subcellular topologies of polypeptides in Streptomyces
- PMID: 29544487
- PMCID: PMC5853079
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-018-0892-0
Comprehensive subcellular topologies of polypeptides in Streptomyces
Abstract
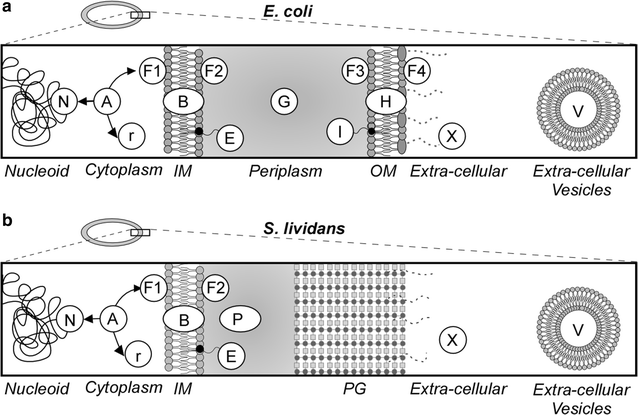
Background: Members of the genus Streptomyces are Gram-positive bacteria that are used as important cell factories to produce secondary metabolites and secrete heterologous proteins. They possess some of the largest bacterial genomes and thus proteomes. Understanding their complex proteomes and metabolic regulation will improve any genetic engineering approach.
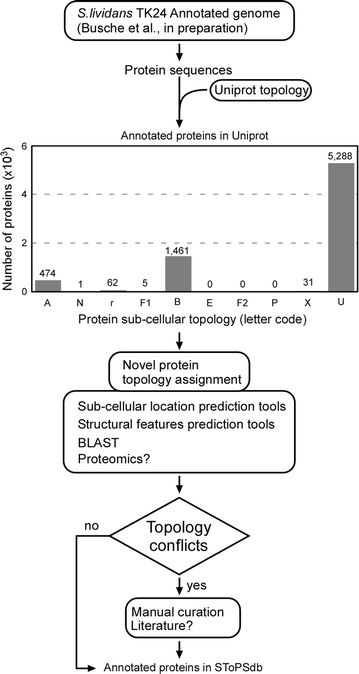
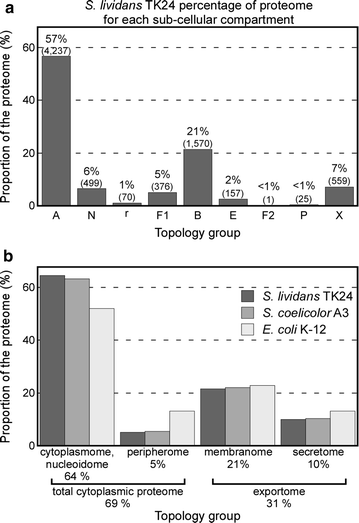
Results: Here, we performed a comprehensive annotation of the subcellular localization of the proteome of Streptomyces lividans TK24 and developed the Subcellular Topology of Polypeptides in Streptomyces database (SToPSdb) to make this information widely accessible. We first introduced a uniform, improved nomenclature that re-annotated the names of ~ 4000 proteins based on functional and structural information. Then protein localization was assigned de novo using prediction tools and edited by manual curation for 7494 proteins, including information for 183 proteins that resulted from a recent genome re-annotation and are not available in current databases. The S. lividans proteome was also linked with those of other model bacterial strains including Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Escherichia coli K-12, based on protein homology, and can be accessed through an open web interface. Finally, experimental data derived from proteomics experiments have been incorporated and provide validation for protein existence or topology for 579 proteins. Proteomics also reveals proteins released from vesicles that bleb off the membrane. All export systems known in S. lividans are also presented and exported proteins assigned export routes, where known.
Conclusions: SToPSdb provides an updated and comprehensive protein localization annotation resource for S. lividans and other streptomycetes. It forms the basis for future linking to databases containing experimental data of proteomics, genomics and metabolomics studies for this organism.
Keywords: Database; Membranome; Peptidoglycan; Protein subcellular localization; Protein subcellular topology; Proteome annotation; S. lividans TK24; Sec system; Secretome; Signal peptide; Sortase; TAT system.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

