Grass Carp Prolactin Gene: Structural Characterization and Signal Transduction for PACAP-induced Prolactin Promoter Activity
- PMID: 29545542
- PMCID: PMC5854708
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-23092-0
Grass Carp Prolactin Gene: Structural Characterization and Signal Transduction for PACAP-induced Prolactin Promoter Activity
Abstract
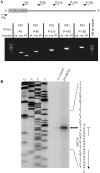
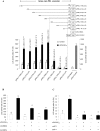
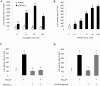
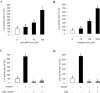
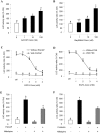
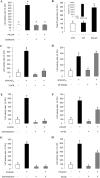
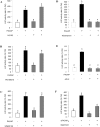
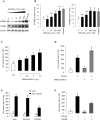
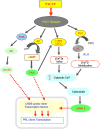
In this study, structural analysis of grass carp prolactin (PRL) gene was performed and the signaling mechanisms for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) regulation of PRL promoter activity were investigated. In αT3-1 cells, PRL promoter activity could be induced by oPACAP38 which was blocked by PACAP antagonist but not the VIP antagonist. The stimulatory effect of oPACAP38 was mimicked by activation of AC/cAMP and voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channel (VSCC) signaling, or induction of Ca2+ entry. In parallel, PACAP-induced PRL promoter activity was negated or inhibited by suppressing cAMP production, inhibiting PKA activity, removal of extracellular Ca2+, VSCC blockade, calmodulin (CaM) antagonism, and inactivation of CaM kinase II. Similar sensitivity to L-type VSCC, CaM and CaM kinase II inhibition were also observed by substituting cAMP analog for oPACAP38 as the stimulant for PRL promoter activity. Moreover, PACAP-induced PRL promoter activity was also blocked by inhibition of PLC signaling, attenuation of [Ca2+]i immobilization via IP3 receptors, and blockade of PI3K/P70S6K pathway. The PACAP-induced PRL promoter activation may involve transactivation of the transcription factor CREB. These results suggest that PACAP can stimulate PRL promoter activation by PAC1 mediated functional coupling of the Ca2+/CaM/CaM kinase II cascades with the AC/cAMP/PKA pathway. Apparently, other signaling pathways, including PLC/IP3 and PI3K/P70S6K cascades, may also be involved in PACAP induction of PRL gene transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential involvement of cAMP/PKA-, PLC/PKC- and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent pathways in GnRH-induced prolactin secretion and gene expression in grass carp pituitary cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 4;15:1399274. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1399274. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38894746 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for PACAP-induced prolactin gene expression in grass carp pituitary cells.J Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;233(1):37-51. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0433. Epub 2017 Jan 27. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28130410
-
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) as a growth hormone (GH)-releasing factor in grass carp. I. Functional coupling of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent signaling pathways in PACAP-induced GH secretion and GH gene expression in grass carp pituitary cells.Endocrinology. 2005 Dec;146(12):5407-24. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0294. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 16123157
-
Cholinergic and peptidergic regulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene expression.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Oct;971:19-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04428.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12438084 Review.
-
PACAP signaling to DREAM: a cAMP-dependent pathway that regulates cortical astrogliogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Apr;39(2):90-100. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8055-2. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19238593 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential involvement of cAMP/PKA-, PLC/PKC- and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent pathways in GnRH-induced prolactin secretion and gene expression in grass carp pituitary cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 4;15:1399274. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1399274. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38894746 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the PACAP/PAC1 Signaling Pathway Accelerates the Repair of Impaired Spatial Memory Caused by an Ultradian Light Cycle.ASN Neuro. 2023 Jan-Dec;15:17590914231169140. doi: 10.1177/17590914231169140. ASN Neuro. 2023. PMID: 37071544 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Mechanisms for IGF-I Regulation by Glucagon in Carp Hepatocytes: Up-Regulation of HNF1α and CREB Expression via Signaling Crosstalk for IGF-I Gene Transcription.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Sep 3;10:605. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00605. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31551932 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinases in the Hypothalamus, Pituitary, and Pineal Gland: An Overview.Int J Endocrinol. 2022 Dec 26;2022:1103346. doi: 10.1155/2022/1103346. eCollection 2022. Int J Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36601542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu, J. C., Baker, R. E., Chow, W., Sun, C. K. & Elsholtz, H. P. Epigenetic mechanisms in the dopamine D2 receptor-dependent inhibition of the prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol19, 1904–1917, doi:10.1210/me.2004-0111 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

