Triptolide induces autophagy and apoptosis through ERK activation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
- PMID: 29545863
- PMCID: PMC5841063
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5830
Triptolide induces autophagy and apoptosis through ERK activation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
Abstract
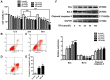
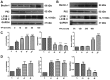
To investigate the effects of triptolide (TPI) on proliferation, autophagy and death in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells, and to elucidate the associated molecular mechanisms, intracellular alterations were analyzed using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and flow cytometry assays. The results of the MTT assay revealed that TPI significantly reduced the MCF-7 cell survival rate when the concentration was >10 nmol/l. TPI activated a caspase cascade reaction by regulating Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), caspase-3 and B-cell lymphoma 2 expression, and promoted programmed cell death via the mitochondrial pathway. The results demonstrated that TPI significantly reduced the cell proliferation rate and viability in a time- and dose-dependent manner, which was confirmed by western blotting and immunofluorescent staining. TPI induced autophagy and influenced p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk)1/2, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) phosphorylation, which resulted in apoptosis. When cells were treated with a combination of TPI and the Erk1/2 inhibitor U0126, the downregulation of P62 and upregulation of Bax were inhibited, which demonstrated that the inhibition of Erk1/2 reversed the autophagy changes induced by TPI. The results indicated that Erk1/2 activation may be a novel mechanism by which TPI induces autophagy and apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. In conclusion, TPI affects the proliferation and apoptosis of MCF-7 cells, potentially via autophagy and p38/Erk/mTOR phosphorylation. The present study offers a novel view of the mechanisms by which TPI regulates cell death.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; breast cancer; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; mechanism; triptolide.
Figures



References
-
- Ikeda H, Taira N, Nogami T, Shien K, Okada M, Shien T, Doihara H, Miyoshi S. Combination treatment with fulvestrant and various cytotoxic agents (doxorubicin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, vinorelbine and 5-fluorouracil) has a synergistic effect in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:2038–2042. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02050.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
