Slug inhibition increases radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line C666-1
- PMID: 29545871
- PMCID: PMC5840900
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5844
Slug inhibition increases radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line C666-1
Abstract
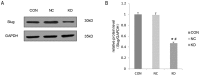
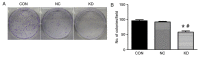
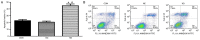
Slug is associated with the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and the main current approach of treatment for NPC is radiotherapy. Hence, the aim of the current study was to determine the effect of Slug silencing on the radiosensitivity of NPC cells. Lentiviral-mediated transfection of Slug RNA interference (RNAi) in NPC cell line C666-1 was performed in vitro. Following Slug inhibition, its expression was detected using western blotting. A clonogenic survival assay and flow cytometry were then performed to evaluate the clonogenic cell survival, cell cycle distribution and apoptosis of C666-1 cells following irradiation. The results indicated that Slug RNAi decreased cell proliferation, and increased cell apoptosis and G0/G1 arrest. Thus, lentiviral-mediated transfection of Slug RNAi enhanced the radiosensitivity of the NPC cell line C666-1, and Slug may therefore be a potential target to improve radiotherapy in treatment of NPC and reduce the radioresistance of NPC.
Keywords: NPC; lentivirus; radiosensitivity; slug.
Figures
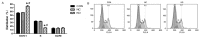
References
-
- Cancer incidence in five continents. Volume VIII. IARC Sci Publ. 2002:1–781. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
