3-Methyladenine and dexmedetomidine reverse lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the inhibition of inflammation and autophagy
- PMID: 29545877
- PMCID: PMC5841051
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5832
3-Methyladenine and dexmedetomidine reverse lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the inhibition of inflammation and autophagy
Abstract
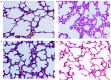
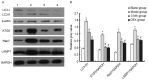
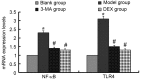
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of 3-methyladenine (3-MA) and dexmedetomidine (DEX) pretreatment on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) and the potential mechanism underlying the effects. LPS was instilled into the trachea of BALB/c mice to induce the ALI model. Solutions of 3-MA or DEX were intravenously injected into the mice 1 h later to establish the 3-MA and DEX groups. On days 1, 3 and 5 after the injections, arterial blood gas analysis was conducted, and the lung wet-dry weight ratio (W/D) was determined. In addition, albumin, cytokine and myeloperoxidase (MPO) contents were evaluated using ELISAs, and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was conducted. Furthermore, western blot analysis was used to evaluate the protein expression levels of microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3)-I, LC3-II, autophagy protein 5 (ATG5), Rab7 and lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1), and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the mRNA expression levels of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Treatment with 3-MA or DEX increased the blood partial pressure of oxygen level compared with that in the model group, and restored the W/D and blood partial pressure of carbon dioxide to normal levels. The content of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and albumin in bronchoalveolar fluid and MPO in lung tissue was significantly decreased in the 3-MA and DEX groups compared with the model group (P<0.05). H&E staining demonstrated that 3-MA and DEX each reversed the ALI. In addition, 3-MA and DEX reduced the protein expression levels of LC3-I, LC3-II, ATG5, Rab7 and LAMP1. Also, RT-qPCR results revealed that NF-κB and TLR4 mRNA expression levels were clearly decreased in the 3-MA and DEX groups compared with the model group. In conclusion, LPS-induced ALI was effectively reversed by treatment with 3-MA and DEX through the reduction of inflammation and autophagy and inhibition of the TLR4-NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: 3-methyladenine; TLR4-NF-κB pathway; acute lung injury; autophagy; dexmedetomidine; inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Griet M, Zelaya H, Mateos MV, Salva S, Juarez GE, de Valdez GF, Villena J, Salvador GA, Rodriguez AV. Soluble factors from Lactobacillus reuteri CRL1098 have anti-Inflammatory effects in acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
