Loss of expression rather than cytoplasmic mislocalization of RUNX3 predicts worse outcome in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29545901
- PMCID: PMC5840764
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.7993
Loss of expression rather than cytoplasmic mislocalization of RUNX3 predicts worse outcome in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
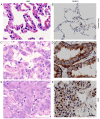
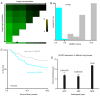
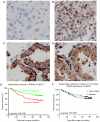
Functional inactivation of human runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) through mutation or epigenetic silencing has been well-documented in many cancerous entities. In addition to gene mutation and promoter hypermethylation, cytoplasmic mislocalization has emerged as another major manifestation of RUNX3 dysfunction in malignancies including breast, colorectal and gastric cancers. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and different RUNX3 expression patterns would have different overall survival (OS), and the associations between different patterns of clinicopathological parameters and clinical outcome. Expressions of RUNX3 and Ki-67 were immunohistochemically detected in normal lung tissue (n=5) and surgically resected tissues from NSCLC patients (n=188). The optimal cutoff of RUNX3 was determined by X-tile software associated with their survival. Apoptotic index in cancerous tissue was evaluated using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labelling method. The prognostic significance of different expression patterns of RUNX3 was determined by means of Kaplan-Meier survival estimates and log-rank tests. It was revealed that loss of RUNX3 expression in NSCLC was correlated with a low cancerous apoptotic index (P<0.001), shorter OS and worse prognosis (P=0.0142), while no statistical difference of apoptotic index (P=0.73) or survival (P=0.3781) was determined between patient subgroups with different localization of RUNX3 expression, which was quite different from the situation demonstrated in other malignancies. In conclusion, loss of expression rather than cytoplasmic mislocalization of RUNX3 predicted worse outcome in NSCLC, which was quite different from what manifested in other cancer types, and thus, the underlying mechanism may deserve further investigation.
Keywords: cytoplasmic mislocalization; non-small cell lung cancer; overall survival; prognosis; runt-related transcription factor 3.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RUNX3/H3K27me3 Co-Expression Defines a Better Prognosis in Surgically Resected Stage I and Postoperative Chemotherapy-Naive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 24;2022:5752263. doi: 10.1155/2022/5752263. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35368900 Free PMC article.
-
[RUNX3 promoter hypermethylation and prognosis of early surgically resected non-small cell lung cancers].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Jul;36(7):650-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2011.07.012. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 21873791 Chinese.
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of RUNX3 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 3;9:2855-65. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76358. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26082616 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter hypermethylation of RASSF1A and RUNX3 genes as an independent prognostic prediction marker in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancers.Lung Cancer. 2007 Oct;58(1):131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.05.011. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Lung Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17606310
-
RUNX3 is multifunctional in carcinogenesis of multiple solid tumors.Oncogene. 2010 May 6;29(18):2605-15. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.88. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20348954 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-106b-5p promotes aggressive progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting RUNX3.Cancer Med. 2019 Nov;8(15):6756-6767. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2511. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31503422 Free PMC article.
-
ASO Author Reflections: RUNX3 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment: Bridging Mechanisms and Clinical Potential.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Sep 8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-18187-8. Online ahead of print. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40921897 No abstract available.
-
RUNX3 levels in human hematopoietic progenitors are regulated by aging and dictate erythroid-myeloid balance.Haematologica. 2020 Apr;105(4):905-913. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.208918. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31171641 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX3 Meets the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Cancer.Cells. 2023 Feb 24;12(5):717. doi: 10.3390/cells12050717. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2/Bcl-2 Coexpression Predicts Worse Survival in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas and Demonstrates Poor Efficacy to Rituximab in Localized Lesions.J Cancer. 2019 May 12;10(9):2006-2017. doi: 10.7150/jca.29807. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31205561 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
