Sizes and Sufficient Quantities of MSC Microspheres for Intrathecal Injection to Modulate Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 29545904
- PMCID: PMC5849255
- DOI: 10.1142/S179398441550004X
Sizes and Sufficient Quantities of MSC Microspheres for Intrathecal Injection to Modulate Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
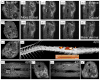
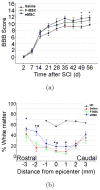
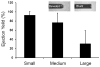
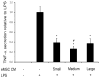
Microencapsulation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in alginate facilitates cell delivery, localization and survival, and modulates inflammation in vivo. However, we found that delivery of the widely used ~0.5 mm diameter encapsulated MSC (eMSC) by intrathecal injection into spinal cord injury (SCI) rats was highly variable. Injections of smaller (~0.2 mm) diameter eMSC into the lumbar spine were much more reproducible and they increased the anti-inflammatory macrophage response around the SCI site. We now report that injection of small eMSC >2 cm caudal from the rat SCI improved locomotion and myelin preservation 8 weeks after rat SCI versus control injections. Because preparation of sufficient quantities of small eMSC for larger studies was not feasible and injection of the large eMSC is problematic, we have developed a procedure to prepare medium-sized eMSC (~0.35 mm diameter) that can be delivered more reproducibly into the lumbar rat spine. The number of MSC incorporated/capsule in the medium sized capsules was ~5-fold greater than that in small capsules and the total yield of eMSC was ~20-fold higher than that for the small capsules. Assays with all three sizes of eMSC capsules showed that they inhibited TNF-α secretion from activated macrophages in co-cultures, suggesting no major difference in their anti-inflammatory activity in vitro. The in vivo activity of the medium-sized eMSC was tested after injecting them into the lumbar spine 1 day after SCI. Histological analyses 1 week later showed that eMSC reduced levels of activated macrophages measured by IB4 staining and increased white matter sparing in similar regions adjacent to the SCI site. The combined results indicate that ~0.35 mm diameter eMSC reduced macrophage inflammation in regions where white matter was preserved during critical early phases after SCI. These techniques enable preparation of eMSC in sufficient quantities to perform pre-clinical SCI studies with much larger numbers of subjects that will provide functional analyses of several critical parameters in rodent models for CNS inflammatory injury.
Keywords: Microcapsules; alginate; inflammation; intrathecal; mesenchymal stem cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Encapsulated Human Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells and a Method to Scale-Up Cell Encapsulation.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 2;12(12):1803. doi: 10.3390/biom12121803. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551231 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed intrathecal delivery of RhoA siRNA to the contused spinal cord inhibits allodynia, preserves white matter, and increases serotonergic fiber growth.J Neurotrauma. 2011 Jun;28(6):1063-76. doi: 10.1089/neu.2010.1568. J Neurotrauma. 2011. PMID: 21443453
-
The immunomodulator decoy receptor 3 improves locomotor functional recovery after spinal cord injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jun 17;13(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0623-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27316538 Free PMC article.
-
Potential risk of clonally expanded amnion mesenchymal stem cell transplants in contused spinal cords.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2018;36(3):387-396. doi: 10.3233/RNN-170786. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29614703
-
Endometrial and Menstrual Blood Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Biological Properties and Clinical Application.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 9;8:497. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00497. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32742977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trends in mesenchymal stem cell clinical trials 2004-2018: Is efficacy optimal in a narrow dose range?Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):17-27. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0202. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31804767 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Use of Algal Polysaccharides for Skin Wound Healing.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(11):1236-1248. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190521120051. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31109271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro inflammatory multi-cellular model of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024 Jan 5;6(1):100432. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2023.100432. eCollection 2024 Mar. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024. PMID: 38288345 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of IL-1β and LPS as optimal activators of monolayer and alginate-encapsulated mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulation using design of experiments and statistical methods.Biotechnol Prog. 2015 Jul-Aug;31(4):1058-70. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2103. Epub 2015 May 28. Biotechnol Prog. 2015. PMID: 25958832 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Encapsulated Human Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells and a Method to Scale-Up Cell Encapsulation.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 2;12(12):1803. doi: 10.3390/biom12121803. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acarregui A, Murua A, Pedraz JL, Orive G, Hernandez RM. Biodrugs. 2012;26:283. - PubMed
-
- Maguire T, Novik E, Schloss R, Yarmush M. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;93:581. - PubMed
-
- Orive G, Santos E, Pedraz JL, Hernandez RM. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014;67–68:3. - PubMed
-
- Zanin MP, Pettingill LN, Harvey AR, Emerich DF, Thanos CG, Shepherd RK. J Control Release. 2012;160:3. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
