Acquired Coagulopathy and Hemorrhage Secondary to Subcutaneous Heparin Prophylaxis
- PMID: 29545958
- PMCID: PMC5818886
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9501863
Acquired Coagulopathy and Hemorrhage Secondary to Subcutaneous Heparin Prophylaxis
Abstract
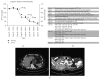
Unfractionated heparin and low-molecular-weight heparins are commonly used as thromboprophylaxis for hospitalized patients. Though generally considered safe at prophylactic doses, cases of catastrophic hemorrhage have been reported. The proposed mechanism involves bioaccumulation of heparin through saturation of the rapid-elimination pathway in its metabolism. We present an unusual case of an average-weight man with metastatic melanoma who suffered hemorrhage with syncope and end-organ damage while on prophylactic three times daily unfractionated heparin. Coagulation studies were consistent with heparin toxicity. Despite administration of protamine, the clearance of heparin was remarkably delayed, as demonstrated by serial coagulation studies. We review the suspected risk factors for heparin bioaccumulation and the emerging understanding of this unusual adverse event involving a nearly ubiquitous medication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Life-threatening hemorrhage following subcutaneous heparin therapy.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009 Feb;5(1):51-4. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s4398. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19436612 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of protamine sulphate on plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor released by intravenous and subcutaneous unfractionated and low molecular weight heparin in man.Thromb Res. 1997 May 15;86(4):343-8. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(97)00078-9. Thromb Res. 1997. PMID: 9187023 Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic effects of subcutaneous heparin use in otolaryngology patients.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Dec;151(6):967-71. doi: 10.1177/0194599814552055. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014. PMID: 25257903
-
[Treatment and prophylaxis of deep venous thrombosis with low molecular weight heparins (meta-analysis of clinical trials)].Medicina (Kaunas). 2003;39(4):352-8. Medicina (Kaunas). 2003. PMID: 12738903 Review. Lithuanian.
-
Are all low molecular weight heparins equivalent in the management of venous thromboembolism?Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2008 Oct;14(4):385-92. doi: 10.1177/1076029608319881. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2008. PMID: 18815137 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosaminoglycan-Protein Interactions and Their Roles in Human Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 9;8:639666. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.639666. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33768117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Spontaneous Intramural Hematoma of the Colon Secondary to Low Molecular Weight Heparin Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 14;12:598661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.598661. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn S. R., Lim W., Dunn A. S., et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2):e195S–e226. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Green D., Hirsh J., Heit J., Prins M., Davidson B., Lensing A. W. Low molecular weight heparin: a critical analysis of clinical trials. Pharmacological Reviews. 1994;46(1):89–109. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

