How UV Light Touches the Brain and Endocrine System Through Skin, and Why
- PMID: 29546369
- PMCID: PMC5905393
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2017-03230
How UV Light Touches the Brain and Endocrine System Through Skin, and Why
Abstract
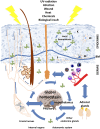
The skin, a self-regulating protective barrier organ, is empowered with sensory and computing capabilities to counteract the environmental stressors to maintain and restore disrupted cutaneous homeostasis. These complex functions are coordinated by a cutaneous neuro-endocrine system that also communicates in a bidirectional fashion with the central nervous, endocrine, and immune systems, all acting in concert to control body homeostasis. Although UV energy has played an important role in the origin and evolution of life, UV absorption by the skin not only triggers mechanisms that defend skin integrity and regulate global homeostasis but also induces skin pathology (e.g., cancer, aging, autoimmune responses). These effects are secondary to the transduction of UV electromagnetic energy into chemical, hormonal, and neural signals, defined by the nature of the chromophores and tissue compartments receiving specific UV wavelength. UV radiation can upregulate local neuroendocrine axes, with UVB being markedly more efficient than UVA. The locally induced cytokines, corticotropin-releasing hormone, urocortins, proopiomelanocortin-peptides, enkephalins, or others can be released into circulation to exert systemic effects, including activation of the central hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, opioidogenic effects, and immunosuppression, independent of vitamin D synthesis. Similar effects are seen after exposure of the eyes and skin to UV, through which UVB activates hypothalamic paraventricular and arcuate nuclei and exerts very rapid stimulatory effects on the brain. Thus, UV touches the brain and central neuroendocrine system to reset body homeostasis. This invites multiple therapeutic applications of UV radiation, for example, in the management of autoimmune and mood disorders, addiction, and obesity.
Figures



References
-
- Elias PM. The skin barrier as an innate immune element. Semin Immunopathol. 2007;29(1):3–14. - PubMed
-
- Feingold KR, Schmuth M, Elias PM. The regulation of permeability barrier homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127(7):1574–1576. - PubMed
-
- Paus R, Langan EA, Vidali S, Ramot Y, Andersen B. Neuroendocrinology of the hair follicle: principles and clinical perspectives. Trends Mol Med. 2014;20(10):559–570. - PubMed
-
- Paus R. The skin and endocrine disorder In: Griffiths CEM, Barker J, Bleiker T, Chalmers R, Creamer D, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. Vol 4 9th ed.Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2016:1–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

