DNA Supercoiling, Topoisomerases, and Cohesin: Partners in Regulating Chromatin Architecture?
- PMID: 29547555
- PMCID: PMC5877745
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030884
DNA Supercoiling, Topoisomerases, and Cohesin: Partners in Regulating Chromatin Architecture?
Abstract
Although our knowledge of chromatin organization has advanced significantly in recent years, much about the relationships between different features of genome architecture is still unknown. Folding of mammalian genomes into spatial domains is thought to depend on architectural proteins, other DNA-binding proteins, and different forms of RNA. In addition, emerging evidence points towards the possibility that the three-dimensional organisation of the genome is controlled by DNA topology. In this scenario, cohesin, CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF), transcription, DNA supercoiling, and topoisomerases are integrated to dictate different layers of genome organization, and the contribution of all four to gene control is an important direction of future studies. In this perspective, we review recent studies that give new insight on how DNA supercoiling shape chromatin structure.
Keywords: CTCF; DNA topology; cohesin; genome organization; topoisomerase; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
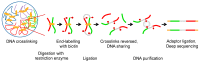
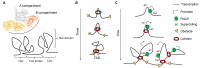
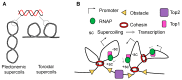
References
-
- Lieberman-Aiden E., van Berkum N.L., Williams L., Imakaev M., Ragoczy T., Telling A., Amit I., Lajoie B.R., Sabo P.J., Dorschner M.O., et al. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science. 2009;326:289–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1181369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

