DNA methylome and transcriptome alterations and cancer prevention by curcumin in colitis-accelerated colon cancer in mice
- PMID: 29547900
- PMCID: PMC6248359
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgy043
DNA methylome and transcriptome alterations and cancer prevention by curcumin in colitis-accelerated colon cancer in mice
Abstract
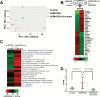
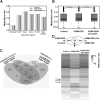
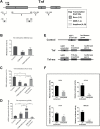
Inflammation is highly associated with colon carcinogenesis. Epigenetic mechanisms could play an important role in the initiation and progression of colon cancer. Curcumin, a dietary phytochemical, shows promising effects in suppressing colitis-associated colon cancer in azoxymethane-dextran sulfate sodium (AOM-DSS) mice. However, the potential epigenetic mechanisms of curcumin in colon cancer remain unknown. In this study, the anticancer effect of curcumin in suppressing colon cancer in an 18-week AOM-DSS colon cancer mouse model was confirmed. We identified lists of differentially expressed and differentially methylated genes in pairwise comparisons and several pathways involved in the potential anticancer effect of curcumin. These pathways include LPS/IL-1-mediated inhibition of RXR function, Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress response, production of NO and ROS in macrophages and IL-6 signaling. Among these genes, Tnf stood out with decreased DNA CpG methylation of Tnf in the AOM-DSS group and reversal of the AOM-DSS induced Tnf demethylation by curcumin. These observations in Tnf methylation correlated with increased and decreased Tnf expression in RNA-seq. The functional role of DNA methylation of Tnf was further confirmed by in vitro luciferase transcriptional activity assay. In addition, the DNA methylation level in a group of inflammatory genes was decreased in the AOM+DSS group but restored by curcumin and was validated by pyrosequencing. This study shows for the first time epigenomic changes in DNA CpG methylation in the inflammatory response from colitis-associated colon cancer and the reversal of their CpG methylation changes by curcumin. Future clinical epigenetic studies with curcumin in inflammation-associated colon cancer would be warranted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The epigenetic effects of aspirin: the modification of histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation in the prevention of colon carcinogenesis in azoxymethane- and dextran sulfate sodium-treated CF-1 mice.Carcinogenesis. 2016 Jun;37(6):616-624. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgw042. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Carcinogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27207670 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics suppress colon tumorigenesis through inhibition of aberrant DNA methylation in an azoxymethane and dextran sulfate sodium colitis model.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jan;110(1):147-156. doi: 10.1111/cas.13880. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30443963 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis by a black lentil water extract through inhibition of inflammatory and immunomodulatory cytokines.Carcinogenesis. 2020 Jul 10;41(6):790-803. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa008. Carcinogenesis. 2020. PMID: 32002542
-
Epigenetics/epigenomics and prevention by curcumin of early stages of inflammatory-driven colon cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Feb;59(2):227-236. doi: 10.1002/mc.23146. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 31820492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E2-EP2 signaling as a node of chronic inflammation in the colon tumor microenvironment.Inflamm Regen. 2017 Mar 1;37:4. doi: 10.1186/s41232-017-0036-7. eCollection 2017. Inflamm Regen. 2017. PMID: 29259703 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enzymatic TET-1 inhibition highlights different epigenetic behaviours of IL-1β and TNFα in tumour progression of OS cell lines.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Oct 2;16(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01745-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39358792 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Targeting of STAT3 Orchestrated Lipid Metabolism in Therapy-Resistant Cancers.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 28;10(8):1118. doi: 10.3390/biom10081118. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32731620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenome and transcriptome study of moringa isothiocyanate in mouse kidney mesangial cells induced by high glucose, a potential model for diabetic-induced nephropathy.AAPS J. 2019 Dec 5;22(1):8. doi: 10.1208/s12248-019-0393-z. AAPS J. 2019. PMID: 31807911
-
Nanomaterials modulate tumor-associated macrophages for the treatment of digestive system tumors.Bioact Mater. 2024 Mar 20;36:376-412. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.003. eCollection 2024 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38544737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics/Epigenomics and Prevention of Early Stages of Cancer by Isothiocyanates.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021 Feb;14(2):151-164. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-20-0217. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021. PMID: 33055265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Söderlund S., et al. (2009)Decreasing time-trends of colorectal cancer in a large cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology, 136, 1561–1567; quiz 1818–1819. - PubMed
-
- Delker D.A., et al. (1998)The role of alcohol dehydrogenase in the metabolism of the colon carcinogen methylazoxymethanol. Toxicol. Sci., 45, 66–71. - PubMed
-
- Robertson K.D. (2005)DNA methylation and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet., 6, 597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

