Low risk of recurrence following artesunate-Sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine plus primaquine for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections in the Republic of the Sudan
- PMID: 29548285
- PMCID: PMC5857106
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-018-2266-9
Low risk of recurrence following artesunate-Sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine plus primaquine for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections in the Republic of the Sudan
Abstract
Background: First-line schizontocidal treatment for uncomplicated malaria in the Republic of the Sudan is artesunate (total dose 12 mg/kg) plus Sulphadoxine/pyrimethamine (25/1.25 mg/kg) (AS/SP). Patients with Plasmodium vivax are also treated with 14 days primaquine (total dose 3.5 mg/kg) (PQ). The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of the national policy.
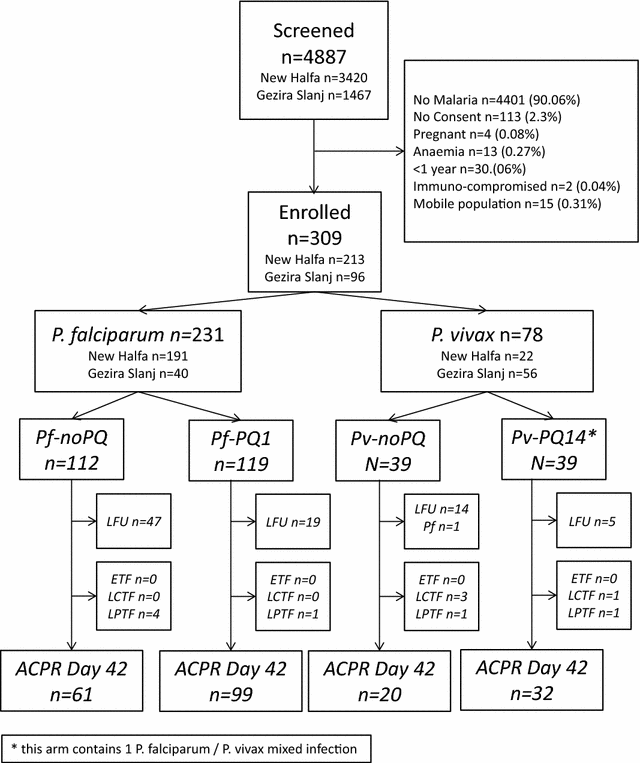
Methods: Patients above 1 year, with microscopy-confirmed, Plasmodium falciparum and/or P. vivax malaria were treated with AS/SP. Patients with P. falciparum were randomized to no primaquine (Pf-noPQ) or a single 0.25 mg/kg dose of PQ (Pf-PQ1). Patients with P. vivax received 14 days unsupervised 3.5 mg/kg PQ (Pv-PQ14) on day 2 or at the end of follow up (Pv-noPQ). Primary endpoint was the risk of recurrent parasitaemia at day 42. G6PD activity was measured by spectrophotometry and the Accessbio Biosensor™.
Results: 231 patients with P. falciparum (74.8%), 77 (24.9%) with P. vivax and 1 (0.3%) patient with mixed infection were enrolled. The PCR corrected cumulative risk of recurrent parasitaemia on day 42 was 3.8% (95% CI 1.2-11.2%) in the Pf-noPQ arm compared to 0.9% (95% CI 0.1-6.0%) in the Pf-PQ1 arm; (HR = 0.25 [95% CI 0.03-2.38], p = 0.189). The corresponding risks of recurrence were 13.4% (95% CI 5.2-31.9%) in the Pv-noPQ arm and 5.3% (95% CI 1.3-19.4%) in the Pv-PQ14 arm (HR 0.36 [95% CI 0.1-2.0], p = 0.212). Two (0.9%) patients had G6PD enzyme activity below 10%, 19 (8.9%) patients below 60% of the adjusted male median. Correlation between spectrophotometry and Biosensor™ was low (rs = 0.330, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: AS/SP remains effective for the treatment of P. falciparum and P. vivax. The addition of PQ reduced the risk of recurrent P. falciparum and P. vivax by day 42, although this did not reach statistical significance. The version of the Biosensor™ assessed is not suitable for routine use. Trial registration https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02592408.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A randomized open-label trial of artesunate- sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine with or without primaquine for elimination of sub-microscopic P. falciparum parasitaemia and gametocyte carriage in eastern Sudan.PLoS One. 2007 Dec 12;2(12):e1311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001311. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 18074034 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Primaquine clears submicroscopic Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes that persist after treatment with sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine and artesunate.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 10;2(10):e1023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001023. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17925871 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nonrandomized controlled trial of artesunate plus sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine with or without primaquine for preventing posttreatment circulation of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jul;57(7):2948-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00139-13. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23587943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of Plasmodium vivax parasitaemia after Plasmodium falciparum infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Jan;19(1):91-101. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30596-6. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30587297 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDd), CareStart qualitative rapid diagnostic test performance, and genetic variants in two malaria-endemic areas in Sudan.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Oct 26;15(10):e0009720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009720. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34699526 Free PMC article.
-
Current investigations on clinical pharmacology and therapeutics of Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jun;222:107788. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107788. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33326820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of quantitative point-of-care tests to measure G6PD activity: An individual participant data meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Mar 25;19(3):e0012864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012864. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40132008 Free PMC article.
-
Novel highly-multiplexed AmpliSeq targeted assay for Plasmodium vivax genetic surveillance use cases at multiple geographical scales.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 11;12:953187. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.953187. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36034708 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphism of the N-terminal region in circumsporozoite surface protein of Plasmodium falciparum field isolates from Sudan.Malar J. 2019 Oct 1;18(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2970-0. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31570093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2016. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

