The association of cardiorespiratory fitness with cardiometabolic factors, markers of inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in Latino youth: findings from the Hispanic Community Children's Health Study/Study of Latino Youth
- PMID: 29548689
- PMCID: PMC6093801
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.02.007
The association of cardiorespiratory fitness with cardiometabolic factors, markers of inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in Latino youth: findings from the Hispanic Community Children's Health Study/Study of Latino Youth
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the relationship of cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) with cardiovascular disease risk factors and a biomarker of endothelial dysfunction (e-selectin) among Hispanic/Latino youth.
Methods: The study included 1380 Hispanic/Latino youths (8-16 years old) from the Hispanic Community Children's Health Study/Study of Latino Youth that enrolled from four cities (Bronx, Chicago, Miami, and San Diego). CRF was assessed by a 3-minute step test that uses postexercise heart rate to estimate maximal oxygen uptake. Regression models assessed differences in cardiometabolic markers across quartiles of CRF, adjusting for potential confounders.
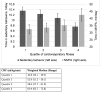
Results: CRF was higher among boys (mean: 57.6 mL per kg/min, 95% confidence interval, 56.8-58.4) compared to girls (mean: 54.7 mL per kg/min, 95% confidence interval, 53.9-55.5). Higher levels of CRF were associated with more favorable levels of cardiometabolic, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction factors (P-values <.001) and independently of physical activity and sedentary time. Compared to the lowest quartile of CRF, the odds of having greater than or equal to two cardiovascular disease risk factors was lower at higher quartiles of CRF, after adjustment for potential confounders.
Conclusions: Among Hispanic/Latino youth, CRF appears to be a strong protective factor for endothelial dysfunction and cardiometabolic risk factors. Strategies to improve CRF may be a useful approach for improving cardiovascular health in youth.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic risk; Cardiorrespiratory fitness; Children; Endothelial function; Hispanic.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sex Differences in Cardiometabolic Risk Factors among Hispanic/Latino Youth.J Pediatr. 2016 Sep;176:121-127.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.05.037. Epub 2016 Jun 22. J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27344220 Free PMC article.
-
Differences across four major US urban areas in metabolic syndrome in the Hispanic Community Children's Health Study/Study of Latino Youth (SOL Youth).Pediatr Obes. 2025 Aug;20(8):e70027. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.70027. Epub 2025 May 19. Pediatr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40384050
-
Objectively Measured Sedentary Behavior, Physical Activity, and Cardiometabolic Risk in Hispanic Youth: Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latino Youth.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Sep 1;103(9):3289-3298. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00356. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29947786 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Criterion-Referenced Cut-Points for Cardiorespiratory Fitness Among Youth: A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2022 Jan;52(1):101-122. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01537-3. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34468952
-
Effect of Physical Activity/Exercise on Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 12;20(2):1407. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021407. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36674162 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exercise Is a Vital Sign.HCA Healthc J Med. 2024 Jun 1;5(3):225-236. doi: 10.36518/2689-0216.1829. eCollection 2024. HCA Healthc J Med. 2024. PMID: 39015584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiorespiratory Fitness: Reference on the Six-Minute Walk Test and Oxygen Consumption in Adolescents from South-Central Chile.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 3;18(5):2474. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052474. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33802300 Free PMC article.
-
Lower adiponectin is associated with higher anthropometry and insulin resistance but not with low cardiorespiratory fitness in adolescents.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Feb;47(2):307-314. doi: 10.1007/s40618-023-02145-w. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 37351836
-
Adiponectin concentration and cardiometabolic risk factors: the moderator role of cardiorespiratory fitness in adolescents.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Nov;183(11):4847-4855. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05761-7. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39251446
References
-
- Laukkanen JA, Kurl S, Salonen R, Rauramaa R, Salonen JT. The predictive value of cardiorespiratory fitness for cardiovascular events in men with various risk profiles: a prospective population-based cohort study. European heart journal. 2004;25(16):1428–37. - PubMed
-
- Blair SN, Kohl HW, 3rd, Paffenbarger RS, Jr, Clark DG, Cooper KH, Gibbons LW. Physical fitness and all-cause mortality. A prospective study of healthy men and women. Jama. 1989;262(17):2395–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

