Phenotype-driven strategies for screening Candida parapsilosis complex for molecular identification
- PMID: 29548715
- PMCID: PMC6328843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjm.2017.11.004
Phenotype-driven strategies for screening Candida parapsilosis complex for molecular identification
Abstract
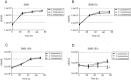
In this study, phenotypic methods presented >80% agreement with the molecular identification of 59 Candida parapsilosis complex. Growth at 15% NaCl or pH 7.0 significantly reduced cfu-counts of Candida orthopsilosis, suggesting these conditions may support the development of phenotypic methods for the differentiation of the cryptic species of C. parapsilosis complex.
Keywords: Candida parapsilosis; Salinity; pH conditions.
Copyright © 2018 Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

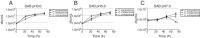
References
-
- Criseo G., Scordino F., Romeo O. Current methods for identifying clinically important cryptic Candida species. J Microbiol Methods. 2015;111:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Sariguzel F.M., Berk E., Koc A.N., Sav H., Aydemir G. Evaluation of chromogenic agar, [corrected] Vitek2 YST and Vitek® MS for identification of Candida strains isolated from blood cultures. Infez Med. 2015;23:318–322. Erratum in: Infez Med. 2016; 24:90. - PubMed
-
- de Hoog G.S., Guarro J., Gené J., Figueiras M.J. 2nd ed. Centraalbureau voor Schinmelculture; Netherlands: 2000. Atlas of Clinical Fungi.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
