Kv2.1 clusters on β-cell plasma membrane act as reservoirs that replenish pools of newcomer insulin granule through their interaction with syntaxin-3
- PMID: 29549124
- PMCID: PMC5936832
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002703
Kv2.1 clusters on β-cell plasma membrane act as reservoirs that replenish pools of newcomer insulin granule through their interaction with syntaxin-3
Abstract
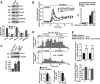
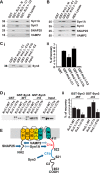
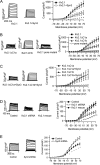
The voltage-dependent K+ (Kv) channel Kv2.1 is a major delayed rectifier in many secretory cells, including pancreatic β cells. In addition, Kv2.1 has a direct role in exocytosis at an undefined step, involving SNARE proteins, that is independent of its ion-conducting pore function. Here, we elucidated the precise step in exocytosis. We previously reported that syntaxin-3 (Syn-3) is the key syntaxin that mediates exocytosis of newcomer secretory granules that spend minimal residence time on the plasma membrane before fusion. Using high-resolution total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy, we now show that Kv2.1 forms reservoir clusters on the β-cell plasma membrane and binds Syn-3 via its C-terminal C1b domain, which recruits newcomer insulin secretory granules into this large reservoir. Upon glucose stimulation, secretory granules were released from this reservoir to replenish the pool of newcomer secretory granules for subsequent fusion, occurring just adjacent to the plasma membrane Kv2.1 clusters. C1b deletion blocked the aforementioned Kv2.1-Syn-3-mediated events and reduced fusion of newcomer secretory granules. These insights have therapeutic implications, as Kv2.1 overexpression in type-2 diabetes rat islets restored biphasic insulin secretion.
Keywords: Kv2.1; insulin secretion; newcomer insulin granule; pancreatic islet; plasma membrane; potassium channel; syntaxin-3; vesicles.
© 2018 Greitzer-Antes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- MacDonald P. E., Sewing S., Wang J., Joseph J. W., Smukler S. R., Sakellaropoulos G., Wang J., Saleh M. C., Chan C. B., Tsushima R. G., Salapatek A. M., and Wheeler M. B. (2002) Inhibition of Kv2.1 voltage-dependent K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44938–44945 10.1074/jbc.M205532200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singer-Lahat D., Sheinin A., Chikvashvili D., Tsuk S., Greitzer D., Friedrich R., Feinshreiber L., Ashery U., Benveniste M., Levitan E. S., and Lotan I. (2007) K+ channel facilitation of exocytosis by dynamic interaction with syntaxin. J. Neurosci. 27, 1651–1658 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4006-06.2007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feinshreiber L., Singer-Lahat D., Friedrich R., Matti U., Sheinin A., Yizhar O., Nachman R., Chikvashvili D., Rettig J., Ashery U., and Lotan I. (2010) Non-conducting function of the Kv2.1 channel enables it to recruit vesicles for release in neuroendocrine and nerve cells. J. Cell Sci. 123, 1940–1947 10.1242/jcs.063719 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

