Emilia-Romagna Study on Pregnancy and Exposure to Antiepileptic drugs (ESPEA): a population-based study on prescription patterns, pregnancy outcomes and fetal health
- PMID: 29549194
- PMCID: PMC6109238
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-317833
Emilia-Romagna Study on Pregnancy and Exposure to Antiepileptic drugs (ESPEA): a population-based study on prescription patterns, pregnancy outcomes and fetal health
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the prevalence of antiepileptic drug (AED) exposure in pregnant women and the comparative risk of terminations of pregnancy (TOPs), spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, major birth defects (MBDs), neonatal distress and small for gestational age (SGA) infants following intrauterine AED exposure in the Emilia Romagna region, Italy (4 459 246 inhabitants on 31 December 2011).
Methods: We identified all deliveries and hospitalised abortions in Emilia Romagna in the period 2009-2011 from the certificate of delivery assistance registry (Certificato di Assistenza al Parto- CedAP) and the hospital discharge card registry, exposure to AEDs from the reimbursed drug prescription registries, MBDs from the regional registry of congenital malformations, and Apgar scores and cases of SGA from the CedAP. Records from different registries were linked.
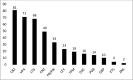
Results: We identified 145 243 pregnancies: 111 284 deliveries, 16 408 spontaneous abortions and 17 551 TOPs. Six hundred and eleven pregnancies (0.42%; 95% Cl 0.39 to 0.46) were exposed to AEDs. In the AED-exposed group 21% of pregnancies ended in TOPs vs 12% in the non-exposed women (OR: 2.24; 95% CI 1.41 to 3.56). Rates of spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, neonatal distress and SGA were comparable. Three hundred and fifty-three babies (0.31%; 95% CI 0.28 to 0.35) were exposed to AEDs during the first trimester. MBD rates were 2.3% in the exposed vs 2.0% in the non-exposed pregnancies (OR: 1.12, 95% CI 0.55 to 2.55).
Conclusion: The Emilia Romagna prevalence of AED exposure in pregnancy was 0.42%, comparable with previous European studies. Rates of spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, neonatal distress, SGA and MBDs following AED exposure were not significantly increased. The rate of TOPs was significantly higher in the AED-exposed women.
Keywords: clinical neurology; epilepsy,anticonvulsants; neuropharmacology; pharmacology.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: BM and FB received a personal fee for an advisory board from EISAI.
Figures
References
-
- Czeizel AE, Bod M, Halász P. Evaluation of anticonvulsant drugs during pregnancy in a population-based Hungarian study. Eur J Epidemiol 1992;8:122–7. - PubMed
-
- Malm H, Martikainen J, Klaukka T, et al. . Finnish Register-Based Study Prescription drugs during pregnancy and lactation-a Finnish register-based study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2003;59:127–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
