Trends and Economic Impact of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in Central Europe: Findings from the Austrian National Database
- PMID: 29549305
- PMCID: PMC5856851
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-23266-w
Trends and Economic Impact of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in Central Europe: Findings from the Austrian National Database
Abstract
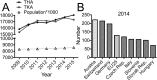
Arthroplasty registers were originally established in Scandinavia to receive clinically relevant information from pooled data, to improve quality and reduce revision surgeries, with socioeconomic benefit. In Austria, where the highest rate of total knee arthroplasties (TKA) per inhabitant of all OECD countries was reached in 2014, arthroplasties are centrally reported since 2009. Study purpose was to perform the first analysis of the Austrian database, aiming to obtain data on trends in arthroplasty in Austria over time in relation to demographic development. Between 2009 and 2015 an almost continuous increase of total hip arthroplasties (THA; 18.052) by 14% and TKA (17.324) by 13% were observed, representing 210 THA and 202 TKA per 100k inhabitants in 2015. A similar increase was found for revision surgeries, with 1.290 re-implanted THA (7.1% of all THA) and 919 re-implanted TKA (5.3% of all TKA) in 2015. Implantation of mega or tumor prosthesis for the knee and hip joint remained constant and was mainly performed in two university hospitals. Patellar resurfacing decreased by 31.6%. Demographic development will further increase the number of primary and revision surgeries. Inclusion of more detailed information on used and revised components was established and will improve efficacy in quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative Epidemiology of Revision Arthroplasty: Failed THA Poses Greater Clinical and Economic Burdens Than Failed TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Jun;473(6):2131-8. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-4078-8. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25467789 Free PMC article.
-
Which Clinical and Patient Factors Influence the National Economic Burden of Hospital Readmissions After Total Joint Arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Dec;475(12):2926-2937. doi: 10.1007/s11999-017-5244-6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 28108823 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in revision hip and knee arthroplasty observations after implementation of a regional joint replacement registry.Can J Surg. 2016 Sep;59(5):304-10. doi: 10.1503/cjs.002916. Can J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27438053 Free PMC article.
-
The changing demographics of total joint arthroplasty recipients in the United States and Ontario from 2001 to 2007.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012 Oct;26(5):637-47. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2012.07.014. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 23218428 Review.
-
Results of total joint arthroplasty and joint preserving surgery in younger patients evaluated by alternative outcome measures.Dan Med J. 2014 Apr;61(4):B4836. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24814600 Review.
Cited by
-
Significant Difference in Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria in Septic Revision between Total Knee Arthroplasty and Total Hip Arthroplasty.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 14;11(2):249. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020249. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203849 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Nutrient Media Compared to Human Synovial Fluid on the Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Gene Expression of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci In Vitro.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;10(7):790. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070790. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209737 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term clinical and radiological outcome of a cementless titanium-coated total knee arthroplasty system.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Feb;144(2):847-853. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-05091-7. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 37831197 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Real-Time Feedback Exercise Therapy in Patients Following Total Hip Arthroplasty: Protocol for a Pilot Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Aug 20;13:e59755. doi: 10.2196/59755. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39163589 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of an in-consult patient decision aid on decisional quality, involvement, and health outcome for patients with severe hip or knee osteoarthritis - a study protocol for a multicentre, cluster randomised controlled trial (PATI-study).BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 2;26(1):584. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08856-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40597226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OECD/European Union. Health at a Glance: Europe 2016. OECD Publishinghttp://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/download/8116231e.pdf?expires=151... (2016).
-
- Hagenbichler, E. Leistungsorientierte Krankenanstaltenfinanzierung (LKF). Austrian Ministry of Health and Women’s Affairshttp://www.bmgf.gv.at/home/Gesundheit/Krankenanstalten/LKF_Leistungsorie... (2011).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

