Long-Term Correction of Diabetes in Mice by In Vivo Reprogramming of Pancreatic Ducts
- PMID: 29550076
- PMCID: PMC5993989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.014
Long-Term Correction of Diabetes in Mice by In Vivo Reprogramming of Pancreatic Ducts
Abstract
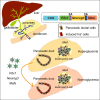
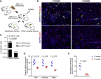
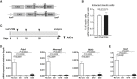
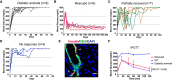
Direct lineage reprogramming can convert readily available cells in the body into desired cell types for cell replacement therapy. This is usually achieved through forced activation or repression of lineage-defining factors or pathways. In particular, reprogramming toward the pancreatic β cell fate has been of great interest in the search for new diabetes therapies. It has been suggested that cells from various endodermal lineages can be converted to β-like cells. However, it is unclear how closely induced cells resemble endogenous pancreatic β cells and whether different cell types have the same reprogramming potential. Here, we report in vivo reprogramming of pancreatic ductal cells through intra-ductal delivery of an adenoviral vector expressing the transcription factors Pdx1, Neurog3, and Mafa. Induced β-like cells are mono-hormonal, express genes essential for β cell function, and correct hyperglycemia in both chemically and genetically induced diabetes models. Compared with intrahepatic ducts and hepatocytes treated with the same vector, pancreatic ducts demonstrated more rapid activation of β cell transcripts and repression of donor cell markers. This approach could be readily adapted to humans through a commonly performed procedure, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), and provides potential for cell replacement therapy in type 1 diabetes patients.
Keywords: Mafa; Neurog3; Pdx1; diabetes; gene therapy; insulin; liver; pancreas; reprogramming; β cell.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Not All Reprogrammed Insulin-Producing Cells Are the Same.Mol Ther. 2018 May 2;26(5):1176-1178. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29678655 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017.
-
- Bolli G.B. Insulin treatment in type 1 diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2006;12(Suppl 1):105–109. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro A.M., Pokrywczynska M., Ricordi C. Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017;13:268–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

