A Distinct Phenotype of Eyes Shut Homolog (EYS)-Retinitis Pigmentosa Is Associated With Variants Near the C-Terminus
- PMID: 29550188
- PMCID: PMC8451245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2018.03.008
A Distinct Phenotype of Eyes Shut Homolog (EYS)-Retinitis Pigmentosa Is Associated With Variants Near the C-Terminus
Abstract
Purpose: Mutations in the eyes shut homolog (EYS) gene are a frequent cause of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (arRP). This study used multimodal retinal imaging to elucidate genotype-phenotype correlations in EYS-related RP (EYS-RP).
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Methods: Multimodal retinal imaging and electrophysiologic testing were assessed for 16 patients with genetic confirmation of EYS-RP.
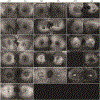
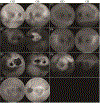
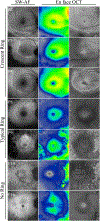
Results: A total of 27 unique EYS variants were identified in 16 patients. Seven patients presented with an unusual crescent-shaped hyperautofluorescent (hyperAF) ring on fundus autofluorescence (FAF) imaging encompassing a large nasal-superior area of the posterior pole. Three patients had a typical circular or oval perifoveal hyperAF ring and 6 patients had no hyperAF ring. Spectral-domain (SD) and en face optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed preserved ellipsoid zone and retinal thickness spatially corresponding to areas within the hyperAF rings. Eleven patients presented with a rod-cone dystrophy on full-field electroretinogram (ffERG), 1 patient presented with cone-rod dystrophy, and 4 patients did not undergo ffERG testing. A significant spatial association was found between EYS variant position and FAF phenotype, with variants occurring at a nucleotide position greater than GRCh37 6:65300137 (c.5617C) being more associated with patients exhibiting hyperAF rings at presentation.
Conclusions: EYS-RP is a heterogeneous manifestation. Variants occurring in positions closer to the C-terminus of EYS are more common in patients presenting with hyperAF rings on FAF imaging.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
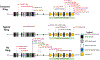
Similar articles
-
Eyes Shut Homolog-Associated Retinal Degeneration: Natural History, Genetic Landscape, and Phenotypic Spectrum.Ophthalmol Retina. 2023 Jul;7(7):628-638. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2023.02.001. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Ophthalmol Retina. 2023. PMID: 36764454
-
Mutations in the EYS gene account for approximately 5% of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cause a fairly homogeneous phenotype.Ophthalmology. 2010 Oct;117(10):2026-33, 2033.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.01.040. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20537394
-
Extending the Spectrum of EYS-Associated Retinal Disease to Macular Dystrophy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 May 1;60(6):2049-2063. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25531. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31074760
-
IMPDH1-associated autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: natural history of novel variant Lys314Gln and a comprehensive literature search.Ophthalmic Genet. 2023 Oct;44(5):437-455. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2023.2215310. Epub 2023 May 31. Ophthalmic Genet. 2023. PMID: 37259572 Review.
-
Non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 Sep;66:157-186. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29597005 Review.
Cited by
-
Phototoxicity avoidance is a potential therapeutic approach for retinal dystrophy caused by EYS dysfunction.JCI Insight. 2024 Apr 22;9(8):e174179. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.174179. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38646933 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Distinctions Between EYS- and USH2A-Associated Retinitis Pigmentosa in an Asian Population.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025 Feb 3;14(2):16. doi: 10.1167/tvst.14.2.16. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 39932467 Free PMC article.
-
Novel compound heterozygous EYS variants may be associated with arRP in a large Chinese pedigree.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;40(6):BSR20193443. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193443. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32436957 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypes Influence Clinical Progression in EYS-Associated Retinitis Pigmentosa.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Jul 8;11(7):6. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.7.6. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35816039 Free PMC article.
-
CERKL-Associated Retinal Dystrophy: Genetics, Phenotype, and Natural History.Ophthalmol Retina. 2023 Oct;7(10):918-931. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Ophthalmol Retina. 2023. PMID: 37331655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berson EL. Retinitis pigmentosa. The Friedenwald Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993;34(5):1659–76. - PubMed
-
- Hartong DT, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006;368(9549):1795–809. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Aziz MM, O’Driscoll CA, Kaye RS, et al.Identification of novel mutations in the ortholog of Drosophila eyes shut gene (EYS) causing autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51(8):4266–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

