Early identification of pneumonia patients at increased risk of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 29550445
- PMCID: PMC7110544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.03.005
Early identification of pneumonia patients at increased risk of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: The rapid and accurate identification of individuals who are at high risk of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection remains a major challenge for the medical and scientific communities. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a risk prediction model for the screening of suspected cases of MERS-CoV infection in patients who have developed pneumonia.
Methods: A two-center, retrospective case-control study was performed. A total of 360 patients with confirmed pneumonia who were evaluated for MERS-CoV infection by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) between September 1, 2012 and June 1, 2016 at King Abdulaziz Medical City in Riyadh and King Fahad General Hospital in Jeddah, were included. According to the rRT-PCR results, 135 patients were positive for MERS-CoV and 225 were negative. Demographic characteristics, clinical presentations, and radiological and laboratory findings were collected for each subject.
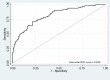
Results: A risk prediction model to identify pneumonia patients at increased risk of MERS-CoV was developed. The model included male sex, contact with a sick patient or camel, diabetes, severe illness, low white blood cell (WBC) count, low alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and high aspartate aminotransferase (AST). The model performed well in predicting MERS-CoV infection (area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUC) 0.8162), on internal validation (AUC 0.8037), and on a goodness-of-fit test (p=0.592). The risk prediction model, which produced an optimal probability cut-off of 0.33, had a sensitivity of 0.716 and specificity of 0.783.
Conclusions: This study provides a simple, practical, and valid algorithm to identify pneumonia patients at increased risk of MERS-CoV infection. This risk prediction model could be useful for the early identification of patients at the highest risk of MERS-CoV infection. Further validation of the prediction model on a large prospective cohort of representative patients with pneumonia is necessary.
Keywords: Early diagnosis; MERS-CoV case definitions; Pneumonia; Saudi Arabia.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed A.E., McClish D.K., Schubert C.M. Accuracy and cost comparison in medical testing using sequential testing strategies. Stat Med. 2011:3416–3430. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed A.E., Schubert C.M., McClish D.K. Reducing cost in sequential testing: a limit of indifference approach. Stat Med. 2013:2715–2727. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed A.E., McClish D.K., Schubert C.M. Believe the extreme (BE) strategy at the optimal point: what strategy will it become? Austin Biom Biostat. 2015;2(3):1022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical