Construction, Expression, and Characterization of rSEA-EGF and In Vitro Evaluation of its Antitumor Activity Against Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- PMID: 29551087
- PMCID: PMC5862366
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033818762910
Construction, Expression, and Characterization of rSEA-EGF and In Vitro Evaluation of its Antitumor Activity Against Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Abstract
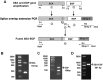
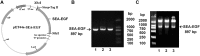
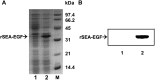
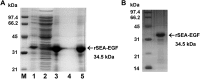
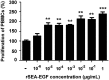
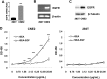
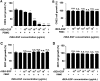
Staphylococcal enterotoxin A is well known as a superantigen and able to be used for cancer immunotherapy. In this study, recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A was genetically conjugated to epidermal growth factor to produce a chimeric protein recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor expressed in Escherichia coli. The recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor protein was purified using Strep-Tactin affinity chromatography and Endotoxin Removal Resin and identified by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electropheresis and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed purified recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor could successfully bind to the human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE2, significantly promote the proliferation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and enhance the secretion of several cytokines that have broad antitumor activities, such as interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-2 . Importantly, recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor significantly inhibited proliferation of CNE2 cells and promoted apoptosis in CNE2 cells when cocultured with peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Finally, both the binding of recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor and the toxicity of recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor-activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells were demonstrated as specific and only effective on high epidermal growth factor receptor-expressing cell lines. In all, our work suggests that recombinant Staphylococcal enterotoxin A-epidermal growth factor serves as a promising novel immunotherapeutic agent. More in vivo and in vitro studies are needed to verify its antitumor potency, as well as investigate the underlying mechanisms in cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; epidermal growth factor; ligand-targeted therapeutics; nasopharyngeal cancer.; staphylococcal enterotoxin A; superantigen fusion protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

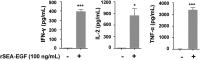
Similar articles
-
Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of TGFαL3-SEB as a Ligand-Targeted Superantigen.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Apr;15(2):215-26. doi: 10.1177/1533034614568753. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 25759426
-
Superantigen-activated mononuclear cells induce apoptosis in transitional cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2005 Sep-Oct;25(5):3565-73. Anticancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16101181
-
Superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 inhibits the growth of bladder cancer.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Sep;81(9):1741-1746. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1350564. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715277
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxins as good candidates for cancer immunotherapy: a systematic review.Ann Ig. 2020 Nov-Dec;32(6):648-663. doi: 10.7416/ai.2019.2386. Ann Ig. 2020. PMID: 33175076
-
SR31747A: a peripheral sigma ligand with potent antitumor activities.Anticancer Drugs. 2004 Feb;15(2):113-8. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200402000-00003. Anticancer Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15075666 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Delivery of 111In Into the Nuclei of EGFR Overexpressing Cells via Modular Nanotransporters With Anti-EGFR Affibody.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 4;11:176. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00176. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32194412 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Chimeric Construct Comprising a Modified Bacterial Superantigen and a Cruzipain Domain Confers Protection Against Trypanosoma cruzi Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 30;11:1279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01279. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32695105 Free PMC article.
-
Novel SPEA Superantigen Peptide Agonists and Peptide Agonist-TGFαL3 Conjugate. In Vitro Study of Their Growth-Inhibitory Effects for Targeted Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10507. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310507. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445686 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

