Dictyostelium Erk2 is an atypical MAPK required for chemotaxis
- PMID: 29551366
- PMCID: PMC5894816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.03.006
Dictyostelium Erk2 is an atypical MAPK required for chemotaxis
Abstract
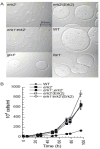
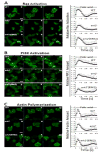
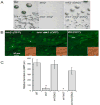
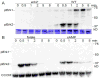
The Dictyostelium genome encodes only two MAPKs, Erk1 and Erk2, and both are expressed during growth and development. Reduced levels of Erk2 expression have been shown previously to restrict cAMP production during development but still allow for chemotactic movement. In this study the erk2 gene was disrupted to eliminate Erk2 function. The absence of Erk2 resulted in a complete loss of folate and cAMP chemotaxis suggesting that this MAPK plays an integral role in the signaling mechanisms involved with this cellular response. However, folate stimulation of early chemotactic responses, such as Ras and PI3K activation and rapid actin filament formation, were not affected by the loss of Erk2 function. The erk2- cells had a severe defect in growth on bacterial lawns but assays of bacterial cell engulfment displayed only subtle changes in the rate of bacterial engulfment. Only cells with no MAPK function, erk1-erk2- double mutants, displayed a severe proliferation defect in axenic medium. Loss of Erk2 impaired the phosphorylation of Erk1 in secondary responses to folate stimulation indicating that Erk2 has a role in the regulation of Erk1 activation during chemotaxis. Loss of the only known Dictyostelium MAPK kinase, MekA, prevented the phosphorylation of Erk1 but not Erk2 in response to folate and cAMP confirming that Erk2 is not regulated by a conventional MAP2K. This lack of MAP2K phosphorylation of Erk2 and the sequence similarity of Erk2 to mammalian MAPK15 (Erk8) suggest that the Dictyostelium Erk2 belongs to a group of atypical MAPKs. MAPK activation has been observed in chemotactic responses in a wide range of organisms but this study demonstrates an essential role for MAPK function in chemotactic movement. This study also confirms that MAPKs provide critical contributions to cell proliferation.
Keywords: Chemotaxis; Dictyostelium; Erk1; Erk2; MAPK.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



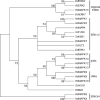
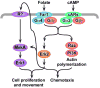
Similar articles
-
Regulatory differences between atypical and typical MAP kinases in Dictyostelium discoideum.Cell Signal. 2025 Jun;130:111701. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111701. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40020888
-
The Dictyostelium MAPK ERK1 is phosphorylated in a secondary response to early developmental signaling.Cell Signal. 2015 Jan;27(1):147-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.10.009. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25451080 Free PMC article.
-
MAP kinases have different functions in Dictyostelium G protein-mediated signaling.Cell Signal. 2010 May;22(5):836-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.008. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20079430 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical MAP kinases - new insights and directions from amoeba.J Cell Sci. 2023 Oct 15;136(20):jcs261447. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261447. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37850857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streamer F mutants and chemotaxis of Dictyostelium.Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):473-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140708. Bioessays. 1992. PMID: 1332700 Review.
Cited by
-
MAPK docking motif in the Dictyostelium Gα2 subunit is required for aggregation and transcription factor translocation.Cell Signal. 2021 Nov;87:110117. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110117. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34418534 Free PMC article.
-
How Phagocytes Acquired the Capability of Hunting and Removing Pathogens From a Human Body: Lessons Learned From Chemotaxis and Phagocytosis of Dictyostelium discoideum (Review).Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 20;9:724940. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.724940. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34490271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A G-protein-coupled chemoattractant receptor recognizes lipopolysaccharide for bacterial phagocytosis.PLoS Biol. 2018 May 25;16(5):e2005754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005754. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29799847 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory differences between atypical and typical MAP kinases in Dictyostelium discoideum.Cell Signal. 2025 Jun;130:111701. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111701. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40020888
-
An Autocrine Negative Feedback Loop Inhibits Dictyostelium discoideum Proliferation through Pathways Including IP3/Ca2.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0134721. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01347-21. Epub 2021 Jun 22. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34154396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meloche S, Pouyssegur J. The ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3227–39. - PubMed
-
- Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 2001;22(2):153–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

