Fusion of fibroblast growth factor 21 to a thermally responsive biopolymer forms an injectable depot with sustained anti-diabetic action
- PMID: 29551712
- PMCID: PMC5945213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.03.015
Fusion of fibroblast growth factor 21 to a thermally responsive biopolymer forms an injectable depot with sustained anti-diabetic action
Abstract
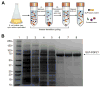
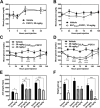
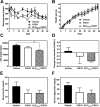
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is under investigation as a type 2 diabetes protein drug, but its efficacy is impeded by rapid in vivo clearance and by costly production methods. To improve the protein's therapeutic utility, we recombinantly expressed FGF21 as a fusion with an elastin-like polypeptide (ELP), a peptide polymer that exhibits reversible thermal phase behavior. Below a critical temperature, ELPs exist as miscible unimers, while above, they associate into a coacervate. The thermal responsiveness of ELPs is retained upon fusion to proteins, which has notable consequences for the production and in vivo delivery of FGF21. First, the ELP acts as a solubility enhancer during E. coli expression, yielding active fusion protein from the soluble cell lysate fraction and eliminating the protein refolding steps that are required for purification of FGF21 from inclusion bodies. Second, the ELP's phase transition behavior is exploited for facile chromatography-free purification of the ELP-FGF21 fusion. Third, the composition and molecular weight of the ELP are designed such that the ELP-FGF21 fusion undergoes a phase transition triggered solely by body heat, resulting in an immiscible viscous phase upon subcutaneous (s.c.) injection and thereby creating an injectable depot. Indeed, a single s.c. injection of ELP-FGF21 affords up to five days of sustained glycemic control in ob/ob mice. The ELP fusion partner massively streamlines production and purification of FGF21, while providing a controlled release method for delivery that reduces the frequency of injection, thereby enhancing the pharmacological properties of FGF21 as a protein drug to treat metabolic disease.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Elastin-like polypeptide; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Recombinant fusion protein; Subcutaneous depot; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
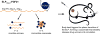


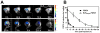
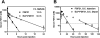
Similar articles
-
A depot-forming glucagon-like peptide-1 fusion protein reduces blood glucose for five days with a single injection.J Control Release. 2013 Nov 28;172(1):144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.07.021. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23928357 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion protein of FGF21 and elastin-like peptide improves wound healing in diabetic mice via inflammation modulation, collagen synthesis, and vascular network formation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 5;982:176953. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176953. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39216743
-
Injectable intratumoral depot of thermally responsive polypeptide-radionuclide conjugates delays tumor progression in a mouse model.J Control Release. 2010 May 21;144(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.01.032. Epub 2010 Jan 31. J Control Release. 2010. PMID: 20117157 Free PMC article.
-
Drug delivery to solid tumors by elastin-like polypeptides.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Dec 30;62(15):1456-67. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.05.004. Epub 2010 May 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 20546809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elastin-like polypeptides: A strategic fusion partner for biologics.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016 Aug;113(8):1617-27. doi: 10.1002/bit.25998. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016. PMID: 27111242 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering the Architecture of Elastin-Like Polypeptides: From Unimers to Hierarchical Self-Assembly.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2020 Mar;3(3):1900164. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201900164. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 34307837 Free PMC article.
-
The construction of elastin-like polypeptides and their applications in drug delivery system and tissue repair.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 11;21(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02184-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37951928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustained release of a GLP-1 and FGF21 dual agonist from an injectable depot protects mice from obesity and hyperglycemia.Sci Adv. 2020 Aug 26;6(35):eaaz9890. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz9890. eCollection 2020 Aug. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32923621 Free PMC article.
-
Programmability and biomedical utility of intrinsically-disordered protein polymers.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Sep;212:115418. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2024.115418. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 39094909 Review.
-
Intra-vitreal αB crystallin fused to elastin-like polypeptide provides neuroprotection in a mouse model of age-related macular degeneration.J Control Release. 2018 Aug 10;283:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 May 18. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29778783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017. U.S. Dept of Health and Human Services; Atlanta: 2017.
-
- Bailey CJ. The Current Drug Treatment Landscape for Diabetes and Perspectives for the Future. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015;98(2):170–184. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Stanislaus S, Chinookoswong N, Lau YY, Hager T, Patel J, Ge H, Weiszmann J, Lu S-C, Graham M, Busby J, Hecht R, Li Y-S, Li Y, Lindberg R, Véniant MM. Acute glucose-lowering and insulin-sensitizing action of FGF21 in insulin-resistant mouse models—association with liver and adipose tissue effects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;297(5):E1105–E1114. - PubMed
-
- Arner P, Pettersson A, Mitchell PJ, Dunbar JD, Kharitonenkov A, Rydén M. FGF21 attenuates lipolysis in human adipocytes – A possible link to improved insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(12):1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Lin Z, Tian H, Lam Karen SL, Lin S, Hoo Ruby CL, Konishi M, Itoh N, Wang Y, Bornstein Stefan R, Xu A, Li X. Adiponectin Mediates the Metabolic Effects of FGF21 on Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Cell Metab. 2013;17(5):779–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

