Sulfate Transporters in Dissimilatory Sulfate Reducing Microorganisms: A Comparative Genomics Analysis
- PMID: 29551997
- PMCID: PMC5840216
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00309
Sulfate Transporters in Dissimilatory Sulfate Reducing Microorganisms: A Comparative Genomics Analysis
Abstract
The first step in the sulfate reduction pathway is the transport of sulfate across the cell membrane. This uptake has a major effect on sulfate reduction rates. Much of the information available on sulfate transport was obtained by studies on assimilatory sulfate reduction, where sulfate transporters were identified among several types of protein families. Despite our growing knowledge on the physiology of dissimilatory sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) there are no studies identifying the proteins involved in sulfate uptake in members of this ecologically important group of anaerobes. We surveyed the complete genomes of 44 sulfate-reducing bacteria and archaea across six phyla and identified putative sulfate transporter encoding genes from four out of the five surveyed protein families based on homology. We did not find evidence that ABC-type transporters (SulT) are involved in the uptake of sulfate in SRM. We speculate that members of the CysP sulfate transporters could play a key role in the uptake of sulfate in thermophilic SRM. Putative CysZ-type sulfate transporters were present in all genomes examined suggesting that this overlooked group of sulfate transporters might play a role in sulfate transport in dissimilatory sulfate reducers alongside SulP. Our in silico analysis highlights several targets for further molecular studies in order to understand this key step in the metabolism of SRMs.
Keywords: CysP; CysZ; DASS; SulP; sulfate transporter; sulfate-reducing microorganisms.
Figures

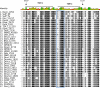

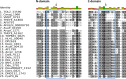





References
-
- Alazard D., Joseph M., Battaglia-Brunet F., Cayol J. L., Ollivier B. (2010). Desulfosporosinus acidiphilus sp. nov.: a moderately acidophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from acid mining drainage sediments: new taxa: Firmicutes (Class Clostridia, Order Clostridiales, Family Peptococcaceae). Extremophiles 14 305–312. 10.1007/s00792-010-0309-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barton L. (ed.) (2013). Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Vol. 8 Berlin: Springer Science+Business Media.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

