Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Branched RRWQWR-Based Peptides as Antibacterial Agents Against Clinically Relevant Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Pathogens
- PMID: 29551999
- PMCID: PMC5840262
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00329
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Branched RRWQWR-Based Peptides as Antibacterial Agents Against Clinically Relevant Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Pathogens
Abstract
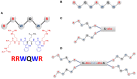
Multidrug resistance of pathogenic bacteria has become a public health crisis that requires the urgent design of new antibacterial drugs such as antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). Seeking to obtain new, lactoferricin B (LfcinB)-based synthetic peptides as viable early-stage candidates for future development as AMPs against clinically relevant bacteria, we designed, synthesized and screened three new cationic peptides derived from bovine LfcinB. These peptides contain at least one RRWQWR motif and differ by the copy number (monomeric, dimeric or tetrameric) and structure (linear or branched) of this motif. They comprise a linear palindromic peptide (RWQWRWQWR), a dimeric peptide (RRWQWR)2KAhx and a tetrameric peptide (RRWQWR)4K2Ahx2C2. They were screened for antibacterial activity against Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212 and ATCC 51575 strains), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 10145 and ATCC 27853 strains) and clinical isolates of two Gram-positive bacteria (Enterococcus faecium and Staphylococcus aureus) and two Gram-negative bacteria (Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa). All three peptides exhibited greater activity than did the reference peptide, LfcinB (17-31), which contains a single linear RRWQWR motif. Against the ATCC reference strains, the three new peptides exhibited minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC50) values of 3.1-198.0 μM and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values of 25-200 μM, and against the clinical isolates, MIC50 values of 1.6-75.0 μM and MBC values of 12.5-100 μM. However, the tetrameric peptide was also found to be strongly hemolytic (49.1% at 100 μM). Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) demonstrated that in the dimeric and tetrameric peptides, the RRWQWR motif is exposed to the pathogen surface. Our results may inform the design of new, RRWQWR-based AMPs.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; antimicrobial peptide; cationic peptide; lactoferricin; lactoferrin; multidrug resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Polyvalence on the Antibacterial Activity of a Synthetic Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin against Healthcare-Associated Infectious Pathogens.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 10;2018:5252891. doi: 10.1155/2018/5252891. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29984236 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic bactericide and antibiotic effects of dimeric, tetrameric, or palindromic peptides containing the RWQWR motif against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 5;9(13):7239-7245. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00708c. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35519960 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Peptides Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibit Antimicrobial Activity against E. coli ATCC 11775, S. maltophilia ATCC 13636 and S. enteritidis ATCC 13076.Molecules. 2017 Mar 12;22(3):452. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030452. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28287494 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Truncated and Polyvalent Peptides Derived from the FKCRRQWQWRMKKGLA Sequence against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923.Molecules. 2017 Jun 14;22(6):987. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060987. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28613262 Free PMC article.
-
Linear and Polyvalent Peptides with Potent Antimicrobial Activity Against Sensitive and Multidrug-Resistant E. c oli Clinical Isolates.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Mar;22(3):e202401734. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401734. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39486005
Cited by
-
Effect of Polyvalence on the Antibacterial Activity of a Synthetic Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin against Healthcare-Associated Infectious Pathogens.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 10;2018:5252891. doi: 10.1155/2018/5252891. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29984236 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent Peptides Internalize HeLa Cells and Kill Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Bacterial Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Aug 4;14(8):793. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14080793. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867987 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic bactericide and antibiotic effects of dimeric, tetrameric, or palindromic peptides containing the RWQWR motif against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 5;9(13):7239-7245. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00708c. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35519960 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial effect and mechanism of bovine lactoferrin against the potato common scab pathogen Streptomyces scabiei.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 25;17(2):e0264094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264094. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35213576 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic antimicrobial peptides: potential templates for anticancer agents.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 24;12:1548603. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1548603. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40342581 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benli M., Yigit N. (2008). Antibacterial activity of venom from funnel web spider Agelena labyrinthica (Araneae: Agelenidae). J. Venom Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 14, 641–650. 10.1590/S.1678-91992008000400007 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

