Novel prognostic scoring system for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 29552174
- PMCID: PMC5840739
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.7966
Novel prognostic scoring system for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
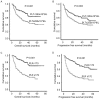
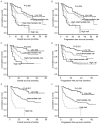
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic values of platelet count (PLT) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), creating a novel prognostic scoring system. A total of 309 patients with newly diagnosed DLBCL were retrospectively analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to determine the optimal threshold values for PLT and PLR, which were 250×109/l and 170, respectively. The patients with PLT ≥250×109/l and PLR ≥170 experienced significantly decreased overall survival (OS) (P<0.001) and progression-free survival (PFS) times (P=0.003, P<0.001) In multivariate analysis, PLR was a significant prognostic factor for OS (P<0.001) and PFS (P=0.003) time, whereas PLT was not a risk factor for PFS or OS time. According to the results of Cox regression analysis, a novel prognostic scoring system was created that combined PLR and β2-microglobulin level with International Prognostic Index value or age-adjusted International Prognostic Index value and the patients were divided into three groups: i) Low-risk patients with a PLR <170, International Prognostic Index (IPI) <2 scores or age-adjusted International Prognostic Index (aaIPI)=0 and normal β2m; ii) high-risk patients with a PLR ≥170, IPI ≥4 or aaIPI=3 and high level of β2m; and iii) intermediate-risk patients. The novel score predicted 5-year OS rates of 86.4, 54.1 and 21.1% in the low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups, respectively (P<0.001). This novel prognostic scoring system may aid the evaluation of patient prognosis and guide treatment.
Keywords: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; platelet; platelet-lymphocyte ratio; prognostic; β2-microglobulin.
Figures

References
-
- Ziepert M, Hasenclever D, Kuhnt E, Glass B, Schmitz N, Pfreundschuh M, Loeffler M. Standard International prognostic index remains a valid predictor of outcome for patients with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2373–2380. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.2493. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
