Telmisartan inhibits NSCLC A549 cell proliferation and migration by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 29552215
- PMCID: PMC5840679
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8002
Telmisartan inhibits NSCLC A549 cell proliferation and migration by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
Expression of angiotensin II (Ang II), a key biological peptide in the renin-angiotensin system, is closely associated with the occurrence and development of cancer. Ang II binds two receptor subtypes, the Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and the AT2R, to mediate a series of biological effects. Telmisartan, a specific AT1R blocker, has been reported to have potential as an anticancer drug for treating renal cancer. In the present study, whether telmisartan had an effect on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell proliferation and migration was investigated. The Cell Counting kit-8 assay revealed that telmisartan significantly inhibited the growth of the NSCLC A549 cell line in a time- and dose-dependent manner. In a transwell assay, telmisartan significantly inhibited cellular invasion and migration. Furthermore, it was determined that the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma was decreased, and that of the pro-apoptotic proteins caspase-3 and Bcl-associated X increased in the A549 cells treated with telmisartan. Additionally, levels of phosphorylated RAC serine/threonine-protein kinase (p-AKT), p-mechanistic target of rapamycin, p70-S6 kinase and cyclin D1 was decreased in the telmisartan-treated group. Therefore, the current study reveals that telmisartan-induced NSCLC apoptosis may be regulated via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway, which indicates that it may be a potential novel drug for clinical NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: angiotensin II; angiotensin II receptor blockers; angiotensin II type 1 receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; phosphoinositide 3-kinase/RAC serine/threonine protein kinase; telmisartan.
Figures


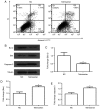

References
-
- Pan ST, Zhou ZW, He ZX, Zhang X, Yang T, Yang YX, Wang D, Qiu JX, Zhou SF. Proteomic response to 5,6-dimethylxanthenone 4-acetic acid (DMXAA, vadimezan) in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells determined by the stable-isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) approach. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:937–968. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kallianos A, Tsimpoukis S, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Charpidou A, Tsioulis I, Trakada G, Porpodis K, Spyratos D, Panoutsopoulos A, et al. Measurement of exhaled alveolar nitrogen oxide in patients with lung cancer: A friend from the past still precious today. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:609–613. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang M, Zhong T, Zhang W, Xiao Z, Hu G, Zhou H, Kuang H. Reduced expression of miR-205-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and invasion in lung cancer A549 cells by upregulation of ZEB2 and downregulation of erbB3. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15:3231–3238. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6398. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
