Colon cancer-induced interleukin-35 inhibits beta-catenin-mediated pro-oncogenic activity
- PMID: 29552287
- PMCID: PMC5844723
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22857
Colon cancer-induced interleukin-35 inhibits beta-catenin-mediated pro-oncogenic activity
Erratum in
-
Correction: Colon cancer-induced interleukin-35 inhibits betacatenin- mediated pro-oncogenic activity.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 3;9(60):31788. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25959. eCollection 2018 Aug 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30167095 Free PMC article.
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Colon cancer-induced interleukin-35 inhibits beta-catenin-mediated pro-oncogenic activity.Oncotarget. 2022 Dec 17;13:1322. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28325. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 36528880 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
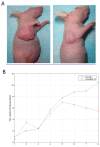
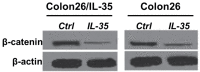
The occurrence and development of colon cancer is closely related to inflammation. Therefore, this study was conducted a current retrospective research to study the effect of IL-35 (interleukin 35), a newly identified anti-infective factor, on colon cancer development. The expression of IL-35 in colon cancer samples and their adjacent normal mucosa by real-time PCR, ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). The effect of IL-35 on patient survival, colon cancer progression, and its effect on Wnt/β-catenine signaling pathway was also assessed. IL-35 is minimally expressed in colon cancer tissues but is highly expressed in adjacent normal tissues. The down-regulation of IL-35 was significantly associated with the American Cancer Joint Committee stage and overall survival of colon cancer patients. The overexpression of IL-35 in colon cancer cells inhibits cell migration, invasion, proliferation, colony formation and cancer stem cells by inhibiting beta-catenin. IL-35 inhibits colon neoplasms in mouse. Our results suggest that IL-35 has an inhibitory effect on the development of colon cancer as a novel prognostic indicator and potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: IL-35; colon cancer; inhibition; metastasis; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that there are no competing interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interleukin-35 expression is associated with colon cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2017 May 10;8(42):71563-71573. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17751. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29069729 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-37 mediates the antitumor activity in colon cancer through β-catenin suppression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):49064-49075. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17093. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28467774 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-35 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is Associated with Tumor Progression.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(4):1839-1851. doi: 10.1159/000495706. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. Retraction in: Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020;54(5):1100. doi: 10.33594/000000302. PMID: 30504722 Retracted.
-
miR-378 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017 Jul 17;22:12. doi: 10.1186/s11658-017-0041-5. eCollection 2017. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28725241 Free PMC article.
-
PMA treated THP-1-derived-IL-6 promotes EMT of SW48 through STAT3/ERK-dependent activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:618-624. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.067. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30243096
Cited by
-
IL35 predicts prognosis in gastric cancer and is associated with angiogenesis by altering TIMP1, PAI1 and IGFBP1.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Dec;10(12):2687-2701. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13005. Epub 2020 Nov 9. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 33064893 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-35 promotes progression of prostate cancer and inhibits anti-tumour immunity.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Oct 7;20:487. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01583-3. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33041668 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation and prognostic implications of intratumor and tumor draining lymph node Foxp3+ T regulatory cells in colorectal cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Mar 16;22(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02205-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35296257 Free PMC article.
-
IL-35 Regulates the Function of Immune Cells in Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 May 21;12:683332. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683332. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-12 Family Cytokines in Cancer and Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 6;13(2):167. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020167. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33418929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patlolla JM, Zhang Y, Li Q, Steele VE, Rao CV. Anti-carcinogenic properties of omeprazole against human colon cancer cells and azoxymethane-induced colonic aberrant crypt foci formation in rats. Int J Oncol. 2012;40:170–75. - PubMed
-
- Amigo-Benavent M, Wang S, Mateos R, Sarria B, Bravo L. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of green coffee and yerba mate extracts, their main hydroxycinnamic acids, methylxanthine and metabolites in different human cell lines. Food and chemical toxicology. 2017 May 17 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Bartlett L, Sloots K, Nowak M, Ho YH. Biofeedback for fecal incontinence: a randomized study comparing exercise regimens. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54:846–56. - PubMed
-
- Nakao S, Hori T, Miura K, Tendo M, Nakata B, Ishikawa T, Hirakawa K. [A case of obstruction due to right-sided colon cancer in which good quality of life was achieved after colonic stenting]. [Article in Japanese] Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2013;40:2059–61. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

