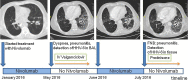
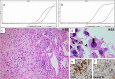
Concomitant Human Herpes Virus 6 and nivolumab-related pneumonitis: Potential pathogenetic insights
- PMID: 29552493
- PMCID: PMC5852387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2018.01.013
Concomitant Human Herpes Virus 6 and nivolumab-related pneumonitis: Potential pathogenetic insights
Abstract
The development of immune system modulating agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has revolutionized cancer treatment. Nivolumab, a human monoclonal antibody against PD-1, has emerged as an efficient treatment for various malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, it is associated with important immune related side-effects, attributed to organ-specific inflammation, such as immune-mediated pneumonitis, a relatively uncommon, albeit potentially fatal adverse event. We herein present the unique case of severe interstitial pneumonitis with concomitant detection of Human Herpes Virus 6 (HHV-6) in a nivolumab treated patient with NSCLC. Potential pathogenetic mechanisms are discussed.
Keywords: Human Herpesvirus 6; Immunotherapy; Lung cancer; Nivolumab.
Figures
References
-
- Martin-Liberal J., Ochoa de Olza M., Hierro C., Gros A., Rodon J., Tabernero J. The expanding role of immunotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;54:74–86. - PubMed
-
- Leventakos K., Mansfield A.S. Advances in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: focus on nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab. BioDrugs. 2016;30:397–405. - PubMed
-
- Tabchi S., Messier C., Blais N. Immune-mediated respiratory adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Opin Oncol. 2016;28:269–277. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson E., Glaser C.A., Forghani B., Amad Z., Wallace M., Armstrong R.W. Evidence of human herpesvirus 6 infection in 4 immunocompetent patients with encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:890–893. - PubMed
-
- Cone R.W. Human herpesvirus 6 as a possible cause of pneumonia. Semin Respir Infect. 1995;10:254–258. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources