Hypoxia Impairs Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Induced Macrophage M1 to M2 Transition
- PMID: 29552603
- PMCID: PMC5854485
- DOI: 10.1142/S2339547817500042
Hypoxia Impairs Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Induced Macrophage M1 to M2 Transition
Abstract
The transition of macrophages from the pro-inflammatory M1 to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype is crucial for the progression of normal wound healing. Persistent M1 macrophages within the injury site may lead to an uncontrolled macrophage-mediated inflammatory response and ultimately a failure of the wound healing cascade, leading to chronic wounds. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been widely reported to promote M1 to M2 macrophage transition; however, it is unclear whether MSCs can drive this transition in the hypoxic environment typically observed in chronic wounds. Here we report on the effect of hypoxia (1% O2) on MSCs' ability to transition macrophages from the M1 to the M2 phenotype. While hypoxia had no effect on MSC secretion, it inhibited MSC-induced M1 to M2 macrophage transition, and suppressed macrophage expression and production of the anti-inflammatory mediator interleukin-10 (IL-10). These results suggest that hypoxic environments may impede the therapeutic effects of MSCs.
Figures
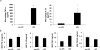
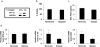
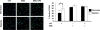
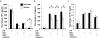
References
-
- Diegelmann RF, Evans MC. Wound healing: an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front Biosci. 2004;9:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Le Blanc K, Mougiakakos D. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:383–396. - PubMed
-
- Sindrilaru A, Peters T, Wieschalka S, Baican C, Baican A, Peter H, Hainzl A, Schatz S, Qi Y, Schlecht A, Weiss JM, Wlaschek M, Sunderkotter C, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. An unrestrained proinflammatory M1 macrophage population induced by iron impairs wound healing in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:985–997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nemeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller BH, Brown JM, Hu X, Jelinek I, Star RA, Mezey E. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15:42–49. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
