A systems approach using OSMAC, Log P and NMR fingerprinting: An approach to novelty
- PMID: 29552652
- PMCID: PMC5851912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2017.10.001
A systems approach using OSMAC, Log P and NMR fingerprinting: An approach to novelty
Abstract
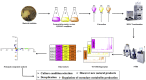
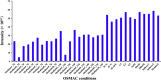
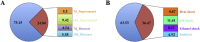
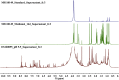
The growing number of sequenced microbial genomes has revealed a remarkably large number of secondary metabolite biosynthetic clusters for which the compounds are still unknown. The aim of the present work was to apply a strategy to detect newly induced natural products by cultivating microorganisms in different fermentation conditions. The metabolomic analysis of 4160 fractions generated from 13 actinomycetes under 32 different culture conditions was carried out by 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. The principal component analysis (PCA) of the 1H NMR spectra showed a clear discrimination between those samples within PC1 and PC2. The fractions with induced metabolites that are only produced under specific growth conditions was identified by PCA analysis. This method allows an efficient differentiation within a large dataset with only one fractionation step. This work demonstrates the potential of NMR spectroscopy in combination with metabolomic data analysis for the screening of large sets of fractions.
Keywords: Metabolites; NMR fingerprints; OSMAC.
Figures







References
-
- Leeds J.A., Schmitt E.K., Krastel P. Recent developments in antibacterial drug discovery: microbe-derived natural products–from collection to the clinic. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;15:211–226. - PubMed
-
- Lew W., Pai M., Oxlade O., Martin D., Menzies D. Initial drug resistance and tuberculosis treatment outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:123–134. - PubMed
-
- Lam K.S. Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9:245–251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

