Integrin-based diffusion barrier separates membrane domains enabling the formation of microbiostatic frustrated phagosomes
- PMID: 29553370
- PMCID: PMC5897098
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.34798
Integrin-based diffusion barrier separates membrane domains enabling the formation of microbiostatic frustrated phagosomes
Abstract
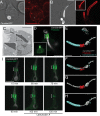
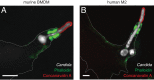
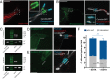
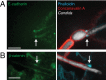
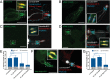
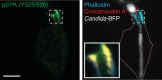
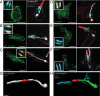
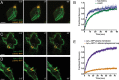
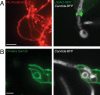
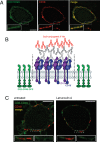
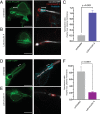
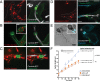
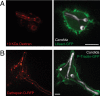
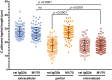
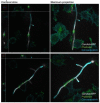
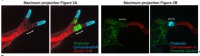
Candida albicans hyphae can reach enormous lengths, precluding their internalization by phagocytes. Nevertheless, macrophages engulf a portion of the hypha, generating incompletely sealed tubular phagosomes. These frustrated phagosomes are stabilized by a thick cuff of F-actin that polymerizes in response to non-canonical activation of integrins by fungal glycan. Despite their continuity, the surface and invaginating phagosomal membranes retain a strikingly distinct lipid composition. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is present at the plasmalemma but is not detectable in the phagosomal membrane, while PtdIns(3)P and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 co-exist in the phagosomes yet are absent from the surface membrane. Moreover, endo-lysosomal proteins are present only in the phagosomal membrane. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching revealed the presence of a diffusion barrier that maintains the identity of the open tubular phagosome separate from the plasmalemma. Formation of this barrier depends on Syk, Pyk2/Fak and formin-dependent actin assembly. Antimicrobial mechanisms can thereby be deployed, limiting the growth of the hyphae.
Keywords: Candida albicans; cell biology; integrins; macrophage; phagocytosis.
© 2018, Maxson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MM, XN, TO, JP, LC, SG No competing interests declared
Figures
References
-
- Bauer C, Herzog V, Bauer MF. Improved Technique for Electron Microscope Visualization of Yeast Membrane Structure. Microscopy and Microanalysis : The Official Journal of Microscopy Society of America, Microbeam Analysis Society, Microscopical Society of Canada. 2001;7:530–534. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ami R, Garcia-Effron G, Lewis RE, Gamarra S, Leventakos K, Perlin DS, Kontoyiannis DP. Fitness and virulence costs of Candida albicans FKS1 hot spot mutations associated with echinocandin resistance. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2011;204:626–635. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

