A role for pericytes in chronic pain?
- PMID: 29553988
- PMCID: PMC6027993
- DOI: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000342
A role for pericytes in chronic pain?
Abstract
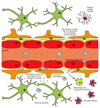
Purpose of review: The importance of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative conditions is becoming increasingly apparent, yet very little is known about these neurovascular functions in nonmalignant disease chronic pain. Neural tissue pericytes play critical roles in the formation and maintenance of the BBB. Herein, we review the important roles of neural pericytes and address their potential role in chronic pain.
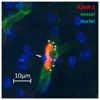
Recent findings: Pericytes are implicated in the function of neural microvasculature, including BBB permeability, neuroimmune factor secretion and leukocyte transmigration. In addition, the multipotent stem cell nature of pericytes affords pericytes the ability to migrate into neural parenchyma and differentiate into pain-associated cell types. These recent findings indicate that pericytes are key players in pathological BBB disruption and neuroinflammation, and as such pericytes may be key players in chronic pain states.
Summary: Pericytes play key roles in pathological processes associated with chronic pain. We propose that pericytes may be a therapeutic target for painful diseases that have associated neural vascular dysfunction. Given the paucity of new pharmacotherapies for chronic pain conditions, we hope that this review inspires researchers to unearth the potential role(s) of pericytes in chronic pain sowing the seeds for future new chronic pain therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role and Molecular Mechanisms of Pericytes in Regulation of Leukocyte Diapedesis in Inflamed Tissues.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 May 7;2019:4123605. doi: 10.1155/2019/4123605. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31205449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune sensors and regulators at the blood brain barrier: focus on toll-like receptors and inflammasomes as mediators of neuro-immune crosstalk and inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Feb 15;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03360-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 39955600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced blood-brain barrier disruption: roles of cyclooxygenase, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and elements of the neurovascular unit.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Nov 25;12:223. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0434-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26608623 Free PMC article.
-
Pericytes support neutrophil transmigration via interleukin-8 across a porcine co-culture model of the blood-brain barrier.Brain Res. 2013 Aug 2;1524:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.05.047. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23769734
-
Tissue plasminogen activator disrupts the blood-brain barrier through increasing the inflammatory response mediated by pericytes after cerebral ischemia.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Nov 18;11(22):10167-10182. doi: 10.18632/aging.102431. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31740626 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

