Temporal trends in Human T-Lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) incidence in Martinique over 25 years (1986-2010)
- PMID: 29554087
- PMCID: PMC5875895
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006304
Temporal trends in Human T-Lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) incidence in Martinique over 25 years (1986-2010)
Abstract
Background: Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) has been discovered in 1980 and has been linked to tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in 1985 in Martinique. There is no data on HAM/TSP incidence trends. We report, in the present work, the temporal trends incidence of HAM/TSP in Martinique over 25 years.
Methods: Martinique is a Caribbean French West Indies island deserved by a unique Neurology Department involved in HAM/TSP diagnosis and management. A registry has been set up since 1986 and patients diagnosed for a HAM/TSP were prospectively registered. Only patients with a definite HAM/TSP onset between 1986 and 2010 were included in the present study. The 25-year study time was stratified in five-year periods. Crude incidence rates with 95% confidence interval (95%CI) were calculated using Poisson distribution for each period. Age-standardized rates were calculated using the direct method and the Martinique population census of 1990 as reference. Standardized incidence rate ratios with 95% CIs and P trends were assessed from simple Poisson regression models. Number of HTLV-1 infection among first-time blood donors was retrospectively collected from the central computer data system of the Martinique blood bank. The HTLV-1 seroprevalence into this population has been calculated for four 5-year periods between 1996 and 2015.
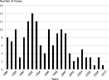
Results: Overall, 153 patients were identified (mean age at onset, 53+/-13.1 years; female:male ratio, 4:1). Crude HAM/TSP incidence rates per 100,000 per 5 years (95%CI) in 1986-1990, 1991-1995, 1996-2000, 2001-2005 and 2006-2010 periods were 10.01 (6.78-13.28), 13.02 (9.34-16.70), 11.54 (8.13-14.95), 4.27 (2.24-6.28) and 2.03 (0.62-3.43). Age-standardized 5-year incidence rates significantly decreased by 69% and 87% in 2001-2005 and 2006-2010 study periods. Patients characteristics did not differ regarding 1986-2000 and 2001-2010 onset periods. Between 1996-2000 and 2011-2015 study periods, the HTLV-1 seroprevalence significantly decreased by 63%.
Conclusion: Martinique faces a sudden and rapid decline of HAM/TSP incidence from 2001 in comparison to 1986-2000 periods. Reduction of HTLV-1 seroprevalence, that may result from transmission prevention strategy, could account for HAM/TSP incidence decrease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- de The G., and Bomford R (1993) An HTLV-I vaccine: why, how, for whom? AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 9:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Hlela C, Shepperd S, Khumalo NP, Taylor GP (2009) The prevalence of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 in the general population is unknown. AIDS Rev 1:205–14. - PubMed
-
- Manns A, Wilks RJ, Murphy EL, Haynes G, Figueroa JP, Barnett M, et al. (1992) A prospective study of transmission by transfusion of HTLV-I and risk factors associated with seroconversion. Int J Cancer 51:886–91. - PubMed
-
- Donegan E, Lee H, Operskalski EA, Shaw GM, Kleinman SH, Busch MP et al. (1994) Transfusion transmission of retroviruses: human T-lymphotropic virus types I and II compared with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Transfusion 34:478–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous