Protective effect of 3-hydroxybutyrate against endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated vascular endothelial cell damage induced by low glucose exposure
- PMID: 29554103
- PMCID: PMC5858752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191147
Protective effect of 3-hydroxybutyrate against endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated vascular endothelial cell damage induced by low glucose exposure
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: The aim of this study was to elucidate the mechanism by which severe hypoglycemia accelerates vascular complications. Furthermore, we assessed the possible protective effect of ketone bodies against the endothelial cell damage caused by glucose deficiency.
Methods: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured at a glucose level of either 0.56 or 5.6 mmol/L with or without 3-hydroxybutyrate (3-HB) supplementation. Cell viability was assessed with a CCK-8 assay and a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay. The activity of caspases was measured using fluorogenic substrates. The expression of genes associated with endothelial cell function and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was evaluated by real-time quantitative PCR. Protein levels of ER stress-related molecules were assessed by Western blotting.
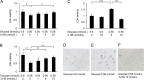
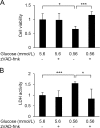
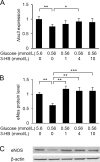
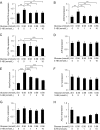
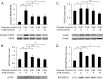
Results: Culture of HUVECs in low-glucose medium for 24 or 48 h resulted in reduction of cell viability accompanied by activation of caspase-3/7 and caspase-8. The addition of a pan caspase inhibitor attenuated the cell death. After incubation in the low-glucose medium, we found reduced mRNA and protein levels of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. ER stress responses mediated by phosphorylation of protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK) and cleavage of activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) were augmented, but X-box binding protein 1 (Xbp1) splicing was reduced. Most of these responses to glucose deficiency were significantly attenuated by supplementation with 3-HB.
Conclusions/interpretation: These observations showed that exposure to low glucose induces ER stress, caspase activation, endothelial cell dysfunction and cell death. The beneficial effects of 3-HB shown in this study suggest that hypoketonemic severe hypoglycemia induced by insulin injections or insulin secretagogue administration may be more harmful than hyperketonemic severe hypoglycemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, Terauchi Y, Noda M. Severe hypoglycaemia and ardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis with bias analysis. BMJ. 2013;347: f4533 doi: 10.1136/bmj.f4533 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wright RJ, Frier BM. Vascular disease and diabetes: is hypoglycaemia an aggravating factor? Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24: 353–63. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.865 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE. The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes 2008;57:3169–76. doi: 10.2337/db08-1084 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109: III27–32. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131515.03336.f8 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

