Limited reverse transcriptase activity of phi29 DNA polymerase
- PMID: 29554297
- PMCID: PMC5909454
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky190
Limited reverse transcriptase activity of phi29 DNA polymerase
Abstract
Phi29 (Φ29) DNA polymerase is an enzyme commonly used in DNA amplification methods such as rolling circle amplification (RCA) and multiple strand displacement amplification (MDA), as well as in DNA sequencing methods such as single molecule real time (SMRT) sequencing. Here, we report the ability of phi29 DNA polymerase to amplify RNA-containing circular substrates during RCA. We found that circular substrates with single RNA substitutions are amplified at a similar amplification rate as non-chimeric DNA substrates, and that consecutive RNA pyrimidines were generally preferred over purines. We observed RCA suppression with higher number of ribonucleotide substitutions, which was partially restored by interspacing RNA bases with DNA. We show that supplementing manganese ions as cofactor supports replication of RNAs during RCA. Sequencing of the RCA products demonstrated accurate base incorporation at the RNA base with both Mn2+ and Mg2+ as cofactors during replication, proving reverse transcriptase activity of the phi29 DNA polymerase. In summary, the ability of phi29 DNA polymerase to accept RNA-containing substrates broadens the spectrum of applications for phi29 DNA polymerase-mediated RCA. These include amplification of chimeric circular probes, such as padlock probes and molecular inversion probes.
Figures
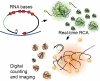

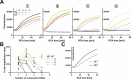
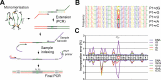
References
-
- Blanco L., Bernad A., Lázaro J.M., Martín G., Garmendia C., Salas M., Bernads A., Lharo J.M., Martins G.. Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the Phage Φ29 DNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1989; 264:8935–8940. - PubMed
-
- Esteban J. a., Salas M., Blanco L.. Fidelity of phi29 DNA Polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993; 268:2719–2726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

