Using the Chinese herb Scutellaria barbata against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: in vitro and in vivo studies
- PMID: 29554903
- PMCID: PMC5859712
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2151-7
Using the Chinese herb Scutellaria barbata against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: in vitro and in vivo studies
Abstract
Background: No animal model studies have been conducted in which the efficacy of herbal compounds has been tested against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Very few antibiotics are available for the treatment of pulmonary infections caused by extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (XDRAB). To find alternative treatments, traditional Chinese herbs were screened for their antimicrobial potential.
Methods: The present study screened 30 herbs that are traditionally used in Taiwan and that are commonly prescribed for heat clearing and detoxification. The herbs with antibacterial activities were analysed by disc diffusion assays, time-kill assays and a murine lung infection model.
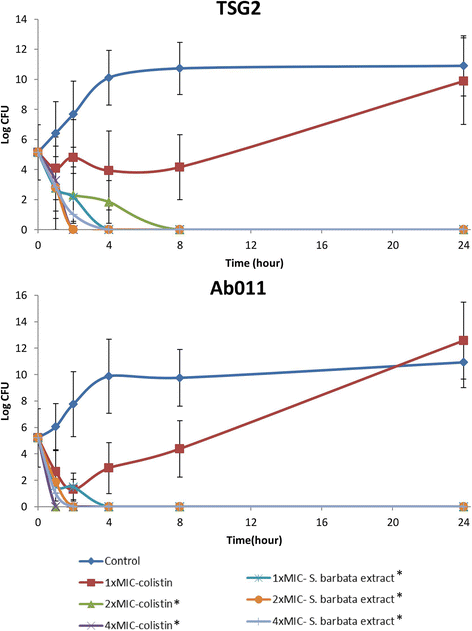
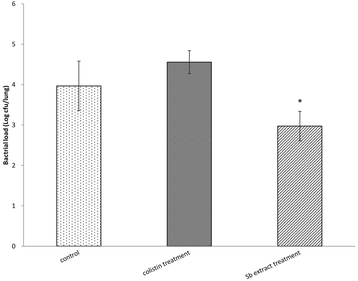
Results: Of the 30 herbs tested, only Scutellaria barbata demonstrated 100% in vitro activity against XDRAB. Furthermore, we compared the antibacterial effect of the S. barbata extract with that of colistin, and the S. barbata extract showed better antibacterial effect. In the XDRAB pneumonia murine model, we compared the antimicrobial effects of the orally administered S. barbata extract (200 mg/kg, every 24 h), the intratracheally administered colistin (75,000 U/kg, every 12 h), and the control group. The bacterial load in the lungs of the treatment group that received the oral S. barbata extract showed a significant decrease in comparison to that in the lungs of the control group. In addition, histopathological examinations also revealed better resolution of perivascular, peribronchial, and alveolar inflammation in the oral S. barbata extract-treated group.
Conclusions: Our in vitro and in vivo data from the animal model support the use of S. barbata as an alternate drug to treat XDRAB pulmonary infections. However, detailed animal studies and clinical trials are necessary to establish the clinical utility of S. barbata in treating XDRAB pulmonary infections.
Keywords: Animal model; Disc diffusion method; Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii; Scutellaria barbata; Time-kill curve.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments in this manuscript did not involve humans. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Use Protocol IACUC of I-Shou University (IACUC-ISU-102032).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

