Structural insights into the inactivation of CRISPR-Cas systems by diverse anti-CRISPR proteins
- PMID: 29554913
- PMCID: PMC5859409
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-018-0504-9
Structural insights into the inactivation of CRISPR-Cas systems by diverse anti-CRISPR proteins
Abstract
A molecular arms race is progressively being unveiled between prokaryotes and viruses. Prokaryotes utilize CRISPR-mediated adaptive immune systems to kill the invading phages and mobile genetic elements, and in turn, the viruses evolve diverse anti-CRISPR proteins to fight back. The structures of several anti-CRISPR proteins have now been reported, and here we discuss their structural features, with a particular emphasis on topology, to discover their similarities and differences. We summarize the CRISPR-Cas inhibition mechanisms of these anti-CRISPR proteins in their structural context. Considering anti-CRISPRs in this way will provide important clues for studying their origin and evolution.
Keywords: Adaptive immune; Anti-CRISPR; CRISPR-Cas system; Structure; Viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
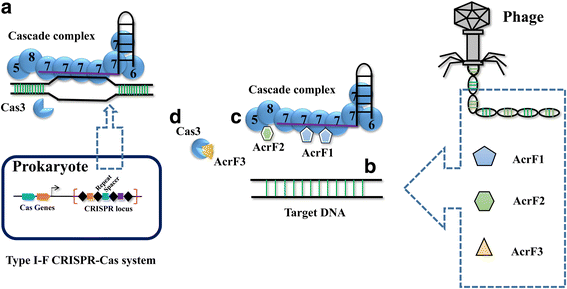
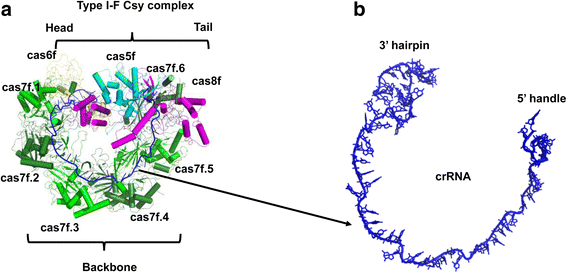
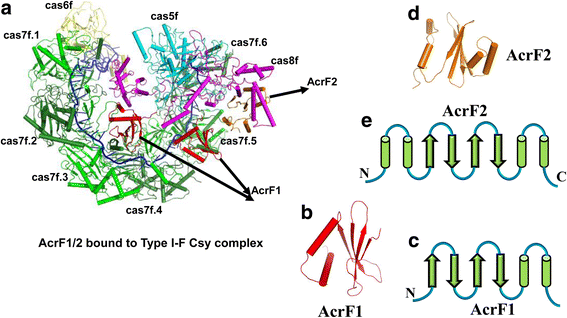
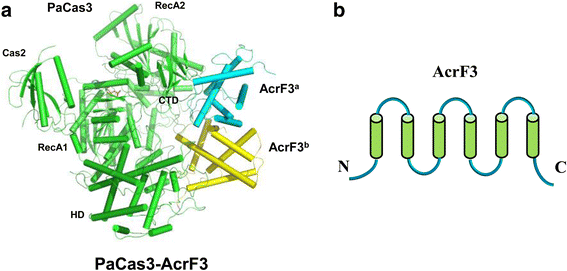
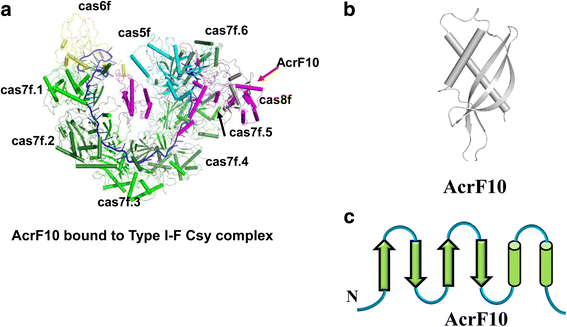
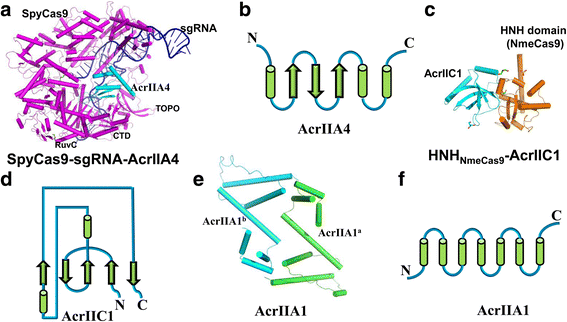
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

