G908R NOD2 variant in a family with sarcoidosis
- PMID: 29554915
- PMCID: PMC5859391
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-018-0748-5
G908R NOD2 variant in a family with sarcoidosis
Abstract
Background: Sarcoidosis is a systemic disease characterized by the formation of immune granulomas in various organs, mainly the lungs and the lymphatic system. Exaggerated granulomatous reaction might be triggered in response to unidentified antigens in individuals with genetic susceptibility. The present study aimed to determine the genetic variants implicated in a familial case of sarcoidosis.
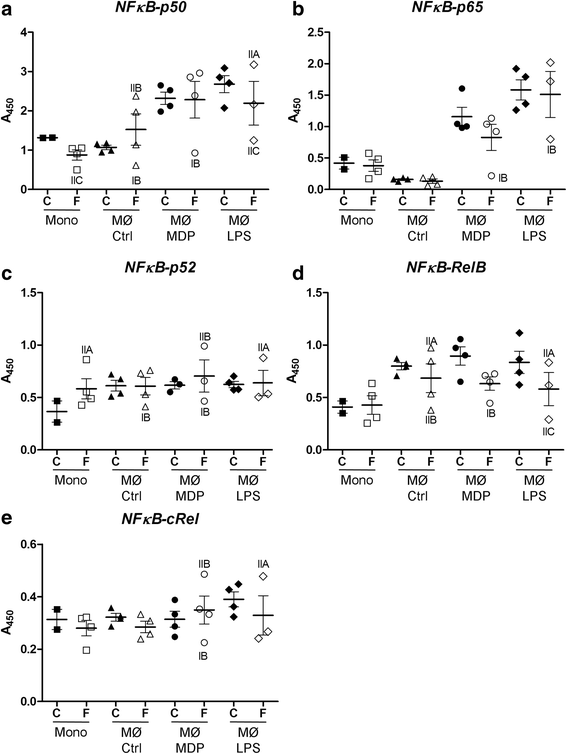
Methods: Sarcoidosis presentation and history, NOD2 profile, NF-κB and cytokine production in blood monocytes/macrophages were evaluated in individuals from a family with late appearance of sarcoidosis.
Results: In the present study, we report a case of familial sarcoidosis with typical thoracic sarcoidosis and carrying the NOD2 2722G > C variant. This variant is associated with the presence of three additional SNPs for the IL17RA, KALRN and EPHA2 genes, which discriminate patients expressing the disease from others. Despite a decrease in NF-κB activity, IL-8 and TNF-A mRNA levels were increased at baseline and in stimulated conditions.
Conclusions: Combination of polymorphisms in the NOD2, IL17RA, EPHA2 and KALRN genes could play a significant role in the development of sarcoidosis by maintaining a chronic pro-inflammatory status in macrophages.
Keywords: Familial sarcoidosis; Genetic susceptibility; NOD2.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study received institutional review board approval (CPP IRN number 00009118) according to French legislation. Written informed consent for all participants was obtained for genetic and biological investigations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

