Interaction of basolateral amygdala, ventral hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex regulates the consolidation and extinction of social fear
- PMID: 29554926
- PMCID: PMC5858134
- DOI: 10.1186/s12993-018-0139-6
Interaction of basolateral amygdala, ventral hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex regulates the consolidation and extinction of social fear
Abstract
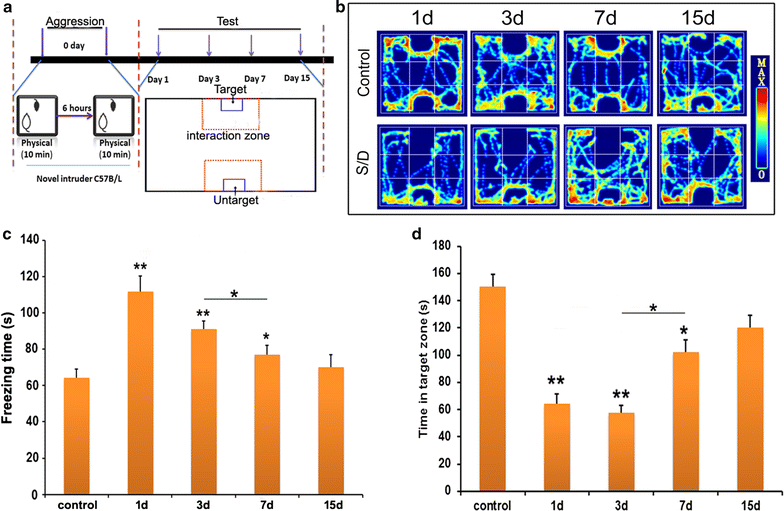
Background: Following a social defeat, the balanced establishment and extinction of aversive information is a beneficial strategy for individual survival. Abnormal establishment or extinction is implicated in the development of mental disorders. This study investigated the time course of the establishment and extinction of aversive information from acute social defeat and the temporal responsiveness of the basolateral amygdala (BLA), ventral hippocampus (vHIP) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in this process.
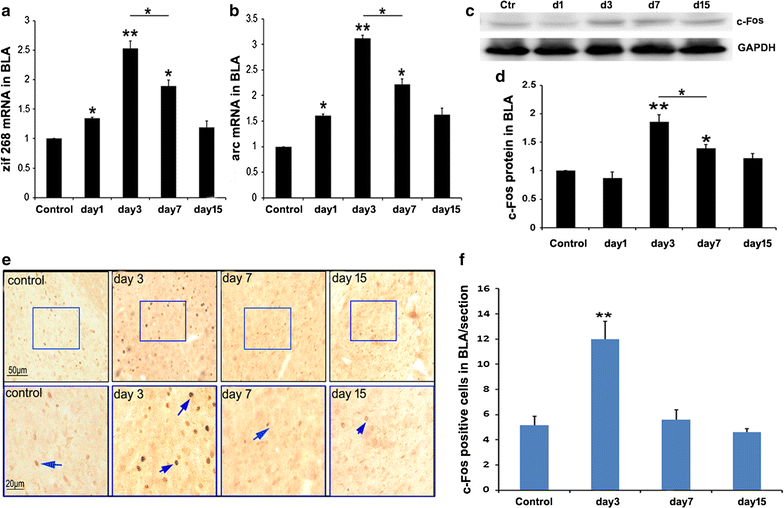
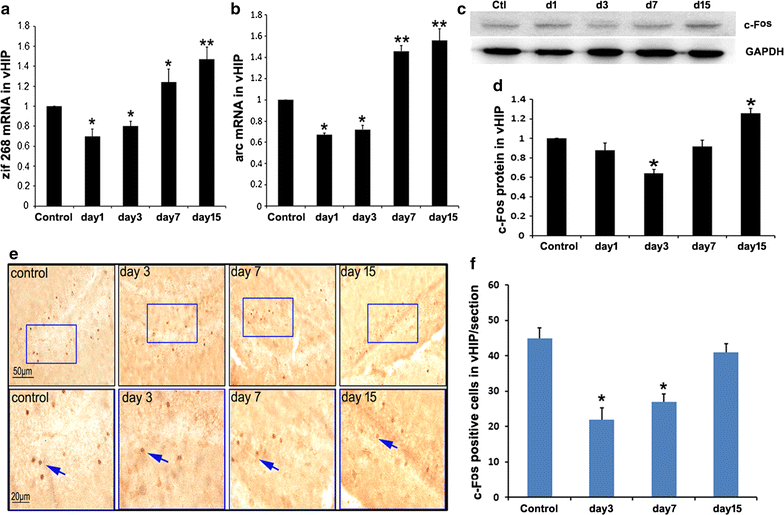
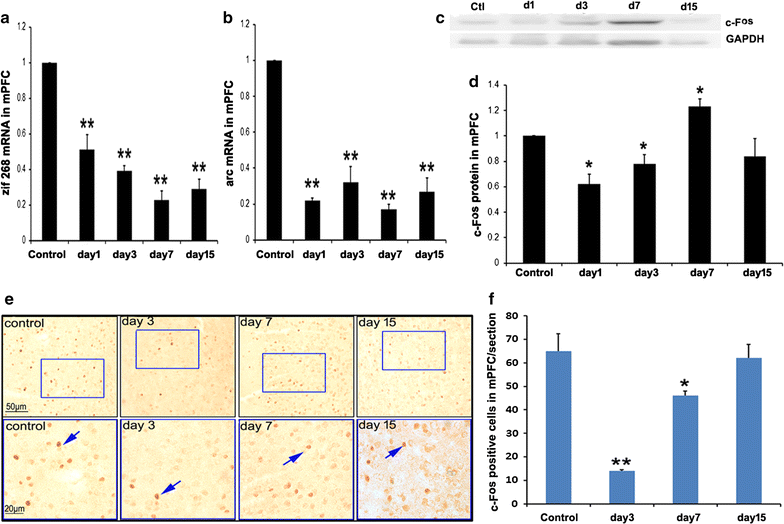
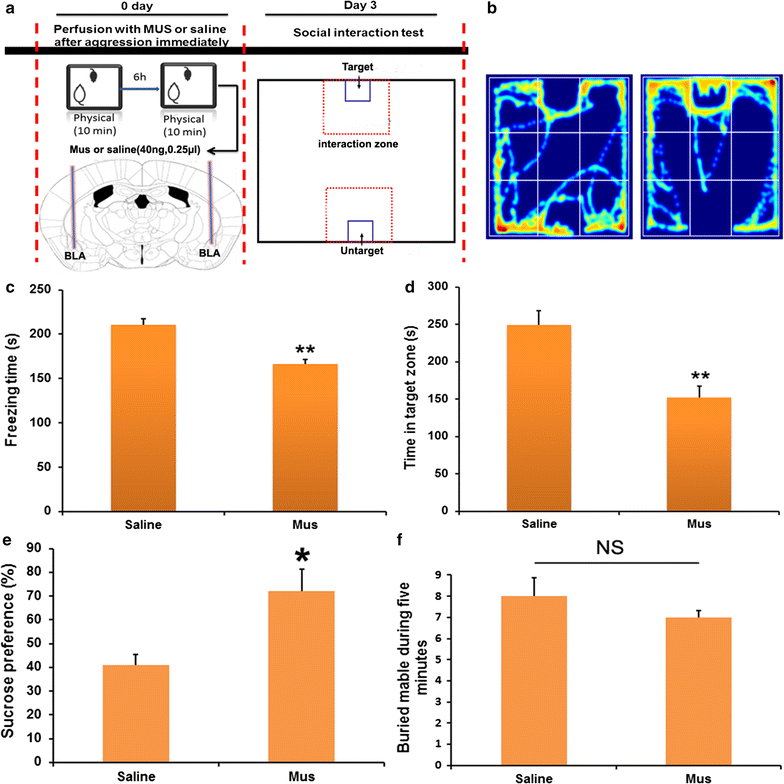
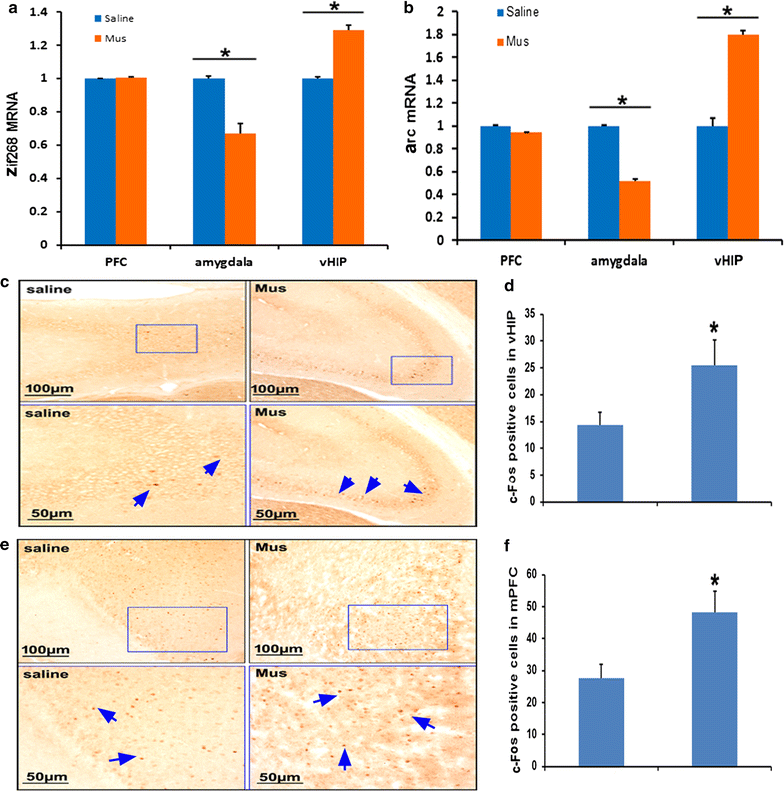
Methods: Mouse models of acute social defeat were established by using the resident-intruder paradigm. To evaluate the engram of social defeat, the intruder mice were placed into the novel context at designated time to test the social behavior. Furthermore, responses of BLA, vHIP and mPFC were investigated by analyzing the expression of immediate early genes, such as zif268, arc, and c-fos.
Results: The results showed after an aggressive attack, aversive memory was maintained for approximately 7 days before gradually diminishing. The establishment and maintenance of aversive stimulation were consistently accompanied by BLA activity. By contrast, vHIP and mPFC response was inhibited from this process. Additionally, injecting muscimol (Mus), a GABA receptor agonist, into the BLA alleviated the freezing behavior and social fear and avoidance. Simultaneously, Mus treatment decreased the zif268 and arc expression in BLA, but it increased their expression in vHIP.
Conclusion: Our data support and extend earlier findings that implicate BLA, vHIP and mPFC in social defeat. The time courses of the establishment and extinction of social defeat are particularly consistent with the contrasting BLA and vHIP responses involved in this process.
Keywords: Basolateral amygdala; Information extinction; Medial prefrontal cortex; Social defeat; Ventral hippocampus.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

