MicroRNA 199a-5p Attenuates Retrograde Transport and Protects against Toxin-Induced Inhibition of Protein Biosynthesis
- PMID: 29555727
- PMCID: PMC5954181
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00548-17
MicroRNA 199a-5p Attenuates Retrograde Transport and Protects against Toxin-Induced Inhibition of Protein Biosynthesis
Abstract
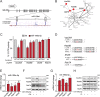
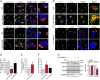
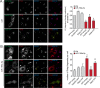
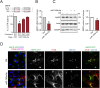
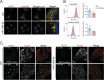
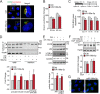
Retrograde transport (RT) allows cells to retrieve receptors and other cellular cargoes for delivery to the Golgi apparatus, contributing to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. This transport route is also commonly used by several bacterial toxins to exert their deleterious actions on eukaryotic cells. While the retrograde transport process has been well characterized, the contribution of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating this cellular transport mechanism remains unknown. Here, we determined that mir-199a and mir-199b, members of the intronic miRNA family, coordinate genes regulating RT and endosome trafficking. We demonstrate that miR-199a-5p attenuates the expression of Vps26A, Rab9B, and M6PR, thereby controlling RT from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Importantly, we found that overexpression of a Vps26A construct resistant to the inhibitory action of miR-199a-5p abrogates the effect of miR-199a-5p on RT. Finally, we demonstrate that miR-199-5p overexpression attenuates Shiga toxin type 1 (Stx1)-mediated inhibition of protein biosynthesis. In summary, our work identifies the first noncoding RNA that influences RT and reduces the inhibition of protein biosynthesis caused by bacterial toxins.
Keywords: bacterial toxins; dynamin; miRNAs; retrograde transport.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
