Prospective evaluation of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA clearance and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission scan in assessing early response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 29555989
- PMCID: PMC5931094
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-018-0026-9
Prospective evaluation of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA clearance and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission scan in assessing early response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Plasma Epstein-Barr virus (pEBV) DNA and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission (PET) reflect tumour burden in advanced NPC. This study hypothesised that a dual endpoint based on assessing pEBV DNA clearance and PET response could predict early drug response.
Methods: Eligible patients underwent a computed tomography (CT) scan and dual PET-CT at baseline, a PET-CT at 4 weeks, and then a CT scan at 10 weeks after starting palliative or induction chemotherapy. Plasma EBV DNA clearance was determined.
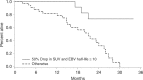
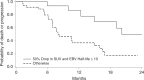
Results: Fifty-eight out of 70 enrolled patients completed all imaging and 50/58 had falling pEBV DNA level, which allowed calculation of the clearance. At a median follow-up of 29.1 months, the dual endpoint (pEBV DNA clearance ≤ 10 days and > 50% drop in sum of SUVmax of target lesions) was an independent indicator of overall survival (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.135, 95% CI = 0.039 to 0.466, p = 0.0015) and progression-free survival (HR = 0.136, 95% CI = 0.048 to 0.385, p = 0002). This dual endpoint could predict subsequent response by Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumours (RECIST) criteria at 10 weeks after chemotherapy.
Conclusions: Early PET-CT response and pEBV DNA clearance could predict survival and subsequent response. This dual endpoint is an innovative tool for assessing early drug response.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01365208.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cao SM, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A phase III multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017;75:14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.12.039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, et al. Induction chemotherapy plus concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase 3, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1509–1520. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30410-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, et al. Preliminary results of trial NPC-0501 evaluating the therapeutic gain by changing from concurrent-adjuvant to induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy, changing from fluorouracil to capecitabine, and changing from conventional to accelerated radiotherapy fractionation in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 2015;121:1328–1338. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29208. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

