High-throughput sequencing of nodal marginal zone lymphomas identifies recurrent BRAF mutations
- PMID: 29556019
- PMCID: PMC6224405
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0082-4
High-throughput sequencing of nodal marginal zone lymphomas identifies recurrent BRAF mutations
Abstract
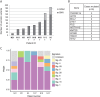
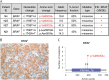
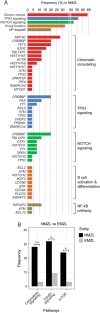
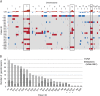
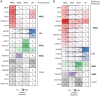
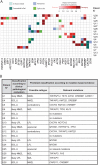
Nodal marginal zone lymphoma (NMZL) is a rare small B-cell lymphoma lacking disease-defining phenotype and precise diagnostic markers. To better understand the mutational landscape of NMZL, particularly in comparison to other nodal small B-cell lymphomas, we performed whole-exome sequencing, targeted high-throughput sequencing, and array-comparative genomic hybridization on a retrospective series. Our study identified for the first time recurrent, diagnostically useful, and potentially therapeutically relevant BRAF mutations in NMZL. Sets of somatic mutations that could help to discriminate NMZL from other closely related small B-cell lymphomas were uncovered and tested on unclassifiable small B-cell lymphoma cases, in which clinical, morphological, and phenotypical features were equivocal. Application of targeted gene panel sequencing gave at many occasions valuable clues for more specific classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017.
-
- Traverse-Glehen A, Bertoni F, Thieblemont C, Zucca E, Coiffier B, Berger F, et al. Nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma: a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Oncology (Williston Park) 2012;26:92–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

