Wnt ligands influence tumour initiation by controlling the number of intestinal stem cells
- PMID: 29556067
- PMCID: PMC5859272
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03426-2
Wnt ligands influence tumour initiation by controlling the number of intestinal stem cells
Abstract
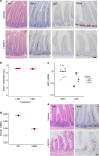
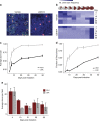
Many epithelial stem cell populations follow a pattern of stochastic stem cell divisions called 'neutral drift'. It is hypothesised that neutral competition between stem cells protects against the acquisition of deleterious mutations. Here we use a Porcupine inhibitor to reduce Wnt secretion at a dose where intestinal homoeostasis is maintained despite a reduction of Lgr5+ stem cells. Functionally, there is a marked acceleration in monoclonal conversion, so that crypts become rapidly derived from a single stem cell. Stem cells located further from the base are lost and the pool of competing stem cells is reduced. We tested whether this loss of stem cell competition would modify tumorigenesis. Reduction of Wnt ligand secretion accelerates fixation of Apc-deficient cells within the crypt leading to accelerated tumorigenesis. Therefore, ligand-based Wnt signalling influences the number of stem cells, fixation speed of Apc mutations and the speed and likelihood of adenoma formation.
Conflict of interest statement
M.E.M. is an employee of Novartis Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kozar, S. et al. Continuous clonal labeling reveals small numbers of functional stem cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas. Cell Stem Cell13, 626–633 (2013).. - PubMed
-
- Farin, H. F., Van Es, J. H. & Clevers, H. Redundant sources of Wnt regulate intestinal stem cells and promote formation of Paneth cells. Gastroenterology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.031 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

