Advanced oxidation protein products inhibit the autophagy of renal tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 29556265
- PMCID: PMC5844045
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.5875
Advanced oxidation protein products inhibit the autophagy of renal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
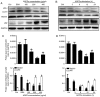
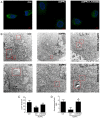
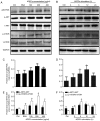
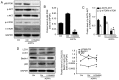
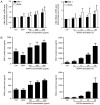
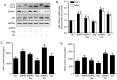
It is well known that autophagy serves a crucial role in renal tubular epithelial cell (RTEC) injury in the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs) also participates in the progression of CKD. However, the effects of AOPPs on autophagy remain unknown. To clarify the underlying mechanism of RTEC injury in CKD, the effect of AOPPs on HK-2 cells, an RTEC cell line, was investigated. The results of the present study revealed that AOPP exposure downregulated the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2-interacting myosin-like coiled-coil protein 1, reduced the conversion of microtubule-associated proteins 1 light chain 3B (LC3)-I to LC3-II and the formation of autophagosomes, and lead to an accumulation of p62. These results suggest that AOPPs may inhibit the autophagic activity of HK-2 cells. Furthermore, the aforementioned changes were mediated by the AOPP-phosphorylated phosphoinositide 3-kinase3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway; this was verified by treatment with LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, which reversed the AOPP-induced changes. The present study also demonstrated that the activation of autophagy with rapamycin led to an improvement in the AOPP-induced overexpression of kidney injury molecule 1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, two biomarkers of RTEC injury, whereas inhibiting autophagy with chloroquine further increased their expression during AOPP treatment. Collectively, these results indicate that AOPPs may inhibit autophagy in RTECs via activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and that autophagy inhibition serves a role in AOPP-induced RTEC injury.
Keywords: advanced oxidation protein products; autophagy; chronic kidney disease; phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway; renal tubular epithelial cell injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human umbilical cord MSC-derived hepatocyte growth factor enhances autophagy in AOPP-treated HK-2 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2765-2773. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8998. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765771 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhanced HK-2 cell autophagy through MicroRNA-145 by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2019 May 15;378(2):198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30880031
-
AGE receptor 1 silencing enhances advanced oxidative protein product-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human kidney proximal tubular epithelial cells via RAGE activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Sep 3;529(4):1201-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.144. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32819586
-
AOPPs and the progression of kidney disease.Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2014 Nov;4(1):102-106. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2014.19. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2014. PMID: 26312159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence of renal tubular epithelial cells in acute kidney injury.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Feb 5;10(1):62. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01831-9. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38316761 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human umbilical cord MSC-derived hepatocyte growth factor enhances autophagy in AOPP-treated HK-2 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2765-2773. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8998. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765771 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products promotes osteoclastogenesis through disruption of redox homeostasis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Dec 14;12(12):1160. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04441-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34907153 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Based on 1H-NMR Reveal the Regulatory Mechanisms of Dietary Methionine Restriction on Splenic Metabolic Dysfunction in Obese Mice.Foods. 2021 Oct 14;10(10):2439. doi: 10.3390/foods10102439. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34681487 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced oxidation protein products attenuate the autophagy-lysosome pathway in ovarian granulosa cells by modulating the ROS-dependent mTOR-TFEB pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 21;15(2):161. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06540-w. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38383507 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Kidney Aging in Diabetes Mellitus.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jul 27;2020:1234059. doi: 10.1155/2020/1234059. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32774664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
