Plant epigenetic mechanisms: role in abiotic stress and their generational heritability
- PMID: 29556426
- PMCID: PMC5845050
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1202-6
Plant epigenetic mechanisms: role in abiotic stress and their generational heritability
Abstract
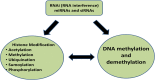
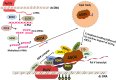
Plants have evolved various defense mechanisms including morphological adaptations, cellular pathways, specific signalling molecules and inherent immunity to endure various abiotic stresses during different growth stages. Most of the defense mechanisms are controlled by stress-responsive genes by transcribing and translating specific genes. However, certain modifications of DNA and chromatin along with small RNA-based mechanisms have also been reported to regulate the expression of stress-responsive genes and constitute another line of defense for plants in their struggle against stresses. More recently, studies have suggested that these modifications are heritable to the future generations as well, thereby indicating their possible role in the evolutionary mechanisms related to abiotic stresses.
Keywords: Abiotic stresses; Adaptations; DNA methylation; Epigenetic mechanism; Plant populations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Response to Abiotic Stress, DNA Methylation Confers EpiGenetic Changes in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 30;10(6):1096. doi: 10.3390/plants10061096. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic control of abiotic stress signaling in plants.Genes Genomics. 2022 Mar;44(3):267-278. doi: 10.1007/s13258-021-01163-3. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Genes Genomics. 2022. PMID: 34515950 Review.
-
Small DNA Methylation, Big Player in Plant Abiotic Stress Responses and Memory.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Dec 10;11:595603. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.595603. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33362826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and epigenetic regulation of stress responses in natural plant populations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1819(2):176-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.08.010. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21914492 Review.
Cited by
-
State-of-the-Art in CRISPR Technology and Engineering Drought, Salinity, and Thermo-tolerant crop plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2022 Mar;41(3):815-831. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02681-w. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Plant Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 33742256 Review.
-
In Response to Abiotic Stress, DNA Methylation Confers EpiGenetic Changes in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 30;10(6):1096. doi: 10.3390/plants10061096. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics data integration reveals link between epigenetic modifications and gene expression in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris) in response to cold.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 17;23(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08312-2. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35176993 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation Strategies to Improve the Resistance of Oilseed Crops to Heat Stress Under a Changing Climate: An Overview.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 15;12:767150. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.767150. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34975951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms behind the phenotypic plasticity associated with Setaria italica water deficit tolerance.Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Aug;109(6):761-780. doi: 10.1007/s11103-022-01273-w. Epub 2022 May 7. Plant Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35524936
References
-
- Abid G, Mingeot D, Muhovski Y, Mergeai G, Aouida M, Abdelkarim S, Jebara M. Analysis of DNA methylation patterns associated with drought stress response in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) using methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism (MSAP) Environ Exp Bot. 2017;142:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.08.004. - DOI
-
- Arıkan B, Özden S, Turgut-Kara N. DNA methylation related gene expression and morphophysiological response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ Exp Bot. 2018;149:17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.01.011. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

