Brachial plexopathy after stereotactic body radiation therapy for apical lung cancer: Dosimetric analysis and preliminary clinical outcomes
- PMID: 29556585
- PMCID: PMC5856987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2017.10.002
Brachial plexopathy after stereotactic body radiation therapy for apical lung cancer: Dosimetric analysis and preliminary clinical outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: The treatment of apical lung tumors with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is challenging due to the proximity of the brachial plexus and the concern for nerve damage.
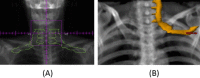
Methods and materials: Between June 2009 and February 2017, a total of 75 consecutive patients underwent SBRT for T1-T3N0 non-small cell lung cancer involving the upper lobe of the lung. All patients were treated with 4-dimensional computed tomography (CT)-based image guided SBRT to a dose of 40 to 60 Gy in 3 to 5 fractions. For dosimetric analysis, only apical tumors as defined by the location of the tumor epicenter superior to the aortic arch were included. The anatomical brachial plexus was delineated using the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group atlas.
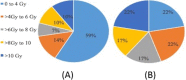
Results: Thirty-one patients with 31 apical lung tumors satisfied the anatomical criteria for inclusion. The median age was 73 years (range, 58-89). The median planning target volume was 26.5 cc (range, 8.2-81.4 cc). The median brachial plexus, brachial plexus maximum dose (Dmax), Dmax per fraction, V22 (cc, 3-4 fractions), V30 (cc, 5 fractions), and biologically effective dose 3 Gy were 15.8 Gy (range, 1.7-66.5 Gy), 3.4 Gy (range, 0.6-14.7 Gy), 0.0 cc (range, 0-0.9 cc), 0.06 cc (range, 0-2.5 cc), and 31.5 Gy (range, 3.3-133.1 Gy), respectively. At a median follow-up of 17 months, the observed incidence of brachial plexopathy was 0%.
Conclusions: There is significant variation in dose to the brachial plexus for patients treated with SBRT for apical lung tumors. Although the incidence of neuropathic symptoms in this series was zero, further attention should be focused on the clinical implications of these findings.
Figures

References
-
- Kirkpatrick J.P., van der Kogel A.J., Schultheiss T.E. Radiation dose-volume effects in the spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:S42–S49. - PubMed
-
- Chen A.M., Wang P.C., Daly M.E. Dose-volume modeling of brachial plexus-associated neuropathy after radiation therapy for head-and-neck cancer: Findings from a prospective screening protocol. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:771–777. - PubMed
-
- Chen A.M., Hall W.H., Li J. Brachial plexus-associated neuropathy after high-dose radiation therapy for head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;84:165–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

